Analysis of water molecules exchange mechanism in 3d cation aquacomplex
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/081323Keywords:
aquacomplexes, 3d-cations, exchange rate of ligand, quantum-chemical calculationAbstract
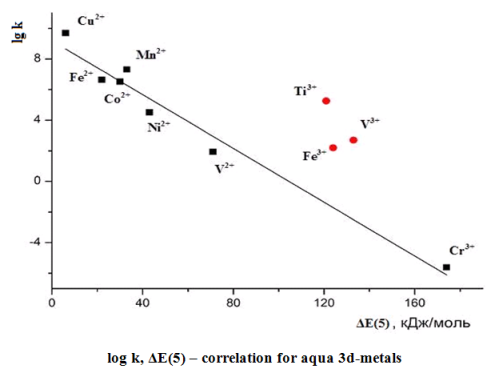
The ligand exchange rate is the significant part of complex compound kinetic. The mechanism of this process may be different. In the article the ability to apply the quantum-chemical method for determination of intermediates type and ligand exchange mechanism have been estimated. Our calculations have shown that the dissociative mechanism of water molecules exchange dominates for the majority of divalent 3d-cations aquacomplexes. It was found that rate of ligand exchange is inversely proportional to the energy logarithm of five intermediate ligand formative as associative mechanisms possible only for Ti2+ aquacomplexes. The associative mechanism is to be place for trivalent cations Ti3+, V3+, Mn3+ and Fe3+ aquacomplexes. Associative compounds of Cr3+ and Co3+ is forbidden and exchange of inner water molecules implement through the complex for such cations dissociative mechanism. This method allow to determine the ligand exchange rate in the complexes which haven’t these values and to estimate the labilite of the short-lived intermediate complexes.
References
Gordon, M. S., Schmidt, M. W. Advances in electronic structure theory: GAMESS a decade later, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2005, p. 1167-1189.
Sereduyk, V. O., Vargaluyk, V. F. Estimation of reliability of quantum-chemical calculations of electronic transitions in aqua complexes of transition metals. Russian Journal of Electrochemistry, 2008, vol. 44, no. 10, p. 1105-1112.
Skopenko, V. V., Savrunski, L. I. Koordynatsiyna khimiya, Кyiv: Lybyd, 1997, 336 p.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2014 Vìsnik Dnìpropetrovsʹkogo unìversitetu. Serìâ Hìmìâ

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

