Synthesis and alkylation of amide obtained by N-Phthaloylglycine and himic acid hydrazide
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/081512Keywords:
hydrazide, himic acid, N-phthaloylglycineAbstract
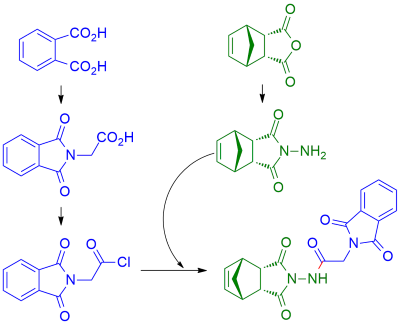
Himic acid hydrazide derivatives are promising in terms of practical use compounds due to their wide range of biological effects (primarily neurotropic activity) and their synthetic potential. Earlier investigated in detail the methods of synthesis of hydrazones, urea, amide and imide derivatives of himic acid hydrazide. Also known diverse biological action of N-Phthaloylglycine, which could serve as an effective protection for the amino group of glycine and has interesting structural features that contribute to the formation of supramolecular complexes. The methodology of synthesis of 2-(Phthalimidoyl)-N-benzyl-N-(4-azatricyclo[5.2.1.02-endo,6-endo]dec-8-ene-3,5-dione-4-yl)acetamide, including obtaining of 2-(Phthalimidoyl)-N-(4-azatricyclo[5.2.1.02-endo,6-endo]dec-8-ene-3,5-dione-4-yl)acetamide based on himic acid hydrazide acid and Phthalylglycyl chloride and alkylation of obtained product. Found that acceptable yield is observed during the alkylation reaction in boiling solution of anhydrous acetone in the presence of excess calcined potassium carbonate. The structure of obtained products was confirmed by analyzing the 1H NMR spectrum.References
Nakamura, T., & Tanji, N. (1992). Production of exo-cis-2,3-norbornanedicarboxylic acid imide. Japan Patent No. JPH049368 (A). Retrive from espacenet.
Scappaticci, K. A. (1991). Treatment of depression. US Patent No. US5011841. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. Retrived from USPTO.
Parenta, E. E., Denceb, C. S., Sharpb, T. L., Welchb, M. J., & Katzenellenbogen, J. A. (2006). Synthesis and biological evaluation of a fluorine-18-labeled nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist, N-(3-[18F]fluoro-4-nitronaphthyl)-cis-5-norbornene-endo-2,3-dicarboxylic imide. Nucl. Med. Biol., 33(5), 615–624. doi:10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2006.04.003
Furdik, M., & Sidoova, E. (1965). Synergists of pyrethrum. XIII. Synthesis of N-aminobicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-ene-2,3-dicarboximide and its derivatives or its 1,4-endoxo analogs. Czech. Acta Fac. Rer. Nat. Univ. Comenianae, Chimia, 9(5). 255–268.
Kas'yan, L. I., Tarabara, I. N., Bondarenko, Ya. S., Shishkina, S. V., Shishkin, O. V., & Musatov, V. I. (2005). Structure and Reactivity of Bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene-endo -5,endo -6-dicarboxylic (endic) Acid Hydrazide. Russ. J. Org. Chem., 41(8), 1122–1131. doi:10.1007/s11178-005-0305-9
Zlenko, O. T., Kasiian, L. I., Mamchur, V. Y., Tarabara I. M., Bondarenko, Ya. S., & Opryshko, V. I. (2007). N-(p-toluene sulfonyl)-N'-(3,5-dioxo-4-azatricyclo[5.2.1.02,6endo]dec-8-en-4-yl)carbamide revealing analgesic, anticonvulsant, tranquilizing and antihypoxic action. Ukraine Patent No. 20676 U. Kyiv, Ukraine: State Enterprise Ukrainian Intellectual Property Institute (Ukrpatent). Retrived from Specialized DB "Inventions (Utility Models) in Ukraine".
Augustin, M., & Reinemann, P. (1973). Reaktion von N-Aminoimiden bicyclischer Dicarbonsaureanhydride. Z. Chem., 13(2), 61–63. doi:10.1002/zfch.19730130210
Hedaya, E., Hinman, R. L., & Theodoropulos, S. (1966). Preparation and Properties of Some New N,N-Biisoimides and Their Cyclic Isomers. Reaction of Biisomaleimides with Dienes. J. Org. Chem., 31(5), 1317–1326. doi:10.1021/jo01343a002
Kasyan, A. O., Krishchik, O. V., Krasnovskaya, O. Yu., & Kasyan L. I. (1998). Amido acids with two frame fragments. Zh. Org. Khim., 34(12), 1802–1806.
Kas’yan, L. I., Tarabara, I. N., Bondarenko, Ya. S., Svyatenko, L. K., & Bondarenko A. V. (2007). Reactions of 4-amino-4-azatricyclo[5.2.1.02,6-endo]dec-8-ene-3,5-dione with dicarboxylic acid anhydrides. Russ. J. Org. Chem., 43(7), 1014–1026. doi:10.1134/S1070428007070135
Kasyan, L. I., & Bondarenko, Ya. S. (2010). Methods of synthesis of tricyclic aminoimides. Visn. Dnipropetr. Univ.: Khim. – Bull. Dnipropetr. Univ.: Chem., 18(16), 45–50.
Bondarenko, Ya. S., & Kasyan, L. I. (2011). Chemical transformations of the product of himic anhydride hydrazinolysis. Visn. Dnipropetr. Univ.: Khim. – Bull. Dnipropetr. Univ.: Chem., 19(17), 50–55.
Kaluđerović, G. N., Kommera, H., Hey-Hawkins, E., Paschkeb R., & Gómez-Ruiz, S. (2010). Synthesis and biological applications of ionic triphenyltin(IV) chloride carboxylate complexes with exceptionally high cytotoxicity. Metallomics, 2, 419–428. doi:10.1039/c0mt00007h
Yan, C., Zhang, J., Liang, T., & Li, Q. (2015). Diorganotin (IV) complexes with 4-nitro-N-phthaloyl-glycine: Synthesis, characterization, antitumor activity and DNA-binding studies. Biomed. Pharmacother., 71, 119–127. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2015.02.027
Matijević-Sosa, J., Samaržija, I., Honović, L., & Jurišić, B. (2008). N-Phthaloyl-glycine-hydroxamic acid as serum iron chelator in rats. Acta Pharm., 58(2), 231–236. doi:10.2478/v10007-008-0010-7
Matijević-Sosa, J., & Cvetnić, Z. (2005). Antimicrobial activity of N-phthaloylamino acid hydroxamates. Acta Pharm., 55(4), 387–399. Retrived from http://hrcak.srce.hr/index.php?show=clanak&id_clanak_jezik=29709
Usifoh, C. O., Lambert, D. M., Wouters, J., & Scriba, G. K. E. (2001). Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of N,N-phthaloyl derivatives of central nervous system inhibitory amino acids. Arch. Pharm., 334(10), 323–331. doi:10.1002/1521-4184(200110)334:10<323::AID-ARDP323>3.0.CO;2-O
Abu Salach, O., Hadad, S., Haj-Yehia, A., Sussan, S., & Bialer, M. (1994) Comparative pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of phthaloyl glycine derivatives with potential antiepileptic activity. Pharm. Res., 11(10), 1429–1434. doi:10.1023/A:1018943906510
Al-Hazimia, H. M., El-Fahamb, A., Ghazzalia, M., Al-Farhana, K. (2012). Microwave irradiation: A facile, scalable and convenient method for synthesis of N-phthaloylamino acids. Arabian J. Chemistry, 5(3), 285–289. doi:10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.06.020
ChemSpider (2015). N-Phthaloylglycine. Retrived from http://www.chemspider.com/ChemicalStructure.19600.html
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2015 Oles Honchar Dnipropetrovsk National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

