Obtaining of barium sulfate from solution formed after desulfation of the active mass of scrap lead-acid batteries
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/081324Keywords:
battery scrap, active mass, desulfation, barium sulfate, barium chloride, barium hydroxide.Abstract
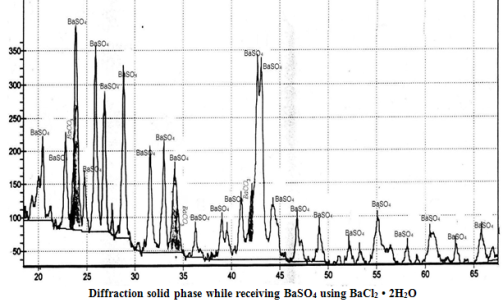
Analyses of literature data about processes for solution utilization formed after desulfation of the active mass of scrap lead-acid batteries is performed. Optimal conditions for obtaining of barium sulfate sediment from ammonium sulfate solute and chemically pure Ba(OH)2×8H2O и BaCl2×2H2O were found experimentally. In laboratory the commercial barium sulfate from sulfate solutions, that are waste of recycling process of battery scrap, with application of chloride and barium hydroxide was production. The possibility of using this product were discussed.
References
Reagents. Potassium sulphate. Specifications. GOST (State standard) 4145-74. IPK Izdatelstvo standartov, 1974, 14 p.
Morachevsky, A. G. Actual problems of disposal of scrap lead-acid batteries. Zhurnal Prikladnoi Khimii, 2003, 76, no. 9, p. 1467-1475.
Morachevsky, A. G. Vaysgant, Z. I., Ugolkov, V. L., Habachev, M. N., Bochagins, E. V., Kalko, O. A., Kuznecova, Yu. S. Regenerative processes in the processing of active masses of scrap lead-acid batteries. Zhurnal Prikladnoi Khimii, 2006, 79, no. 2, p. 242-250.
Morachevsky, A. G., Vaysgant, Z. I., Korelyakov, A. V. Ecological problems of collection and recycling of secondary lead materials. Zhurnal Prikladnoi Khimii, 2000, 73, no. 7, p. 1125-1130.
Morachevsky, A. G. Physico-chemical and technological research desulfation process of lead materials. Zhurnal Prikladnoi Khimii, 1998, 71, no. 6, p. 881-890.
Morachevsky, A. G. Physico-chemistry of lead recycling process, SPb: Bulletin of SPbPU, 2009, 270 p.
Kalko, O. A., Kuznecova, Yu. S., Kunina, N. V. Recycling solutions after desulfation active masses of scrap lead-acid batteries. Bezopasnost' zhiznedejatel'nosti, 2011, no. 5, p.44-48.
Kogan, M. S. Recycling sulphate-oxide fraction scrap lead-acid batteries in the conditions of small-scale industries. Ph.D. thesis, St. Petersburg, 1994, 14 p.
Morachevsky, A. G., Vaysgant, Z. I., Kalko, O. A., Klebanov E. B., Novikova, N. Yu. Recycling solutions after desulfation of lead materials sodium hydroxide. Zhurnal Prikladnoi Khimii, 1997, 70, no. 1, p. 167-168.
Morachevsky, A. G., Kogan, M. S., Demidov, A. I., Vaysgant, Z. I. About regeneration of solutions of sodium hydroxide after desulfation of lead materials. Zhurnal Prikladnoi Khimii. 1993, 66, no. 9, p. 2101-2103.
Hegay, L.D. Lead accumulators: condition, problems, decisions, Vladivostok: Dalnauka, 2005, 256 p.
Reagents. Potassium sulphate. Specifications. GOST (State standard) 4145-74. IPK Izdatelstvo standartov, 1974, 14 p.
Potassium sulfate. Technical conditions (TU) 2184-093-43499406-01.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2014 Vìsnik Dnìpropetrovsʹkogo unìversitetu. Serìâ Hìmìâ

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

