THEORETICAL STUDY OF THE PHOSPHATE UNITS STABILITY BY THE DFT B3LYP/6-311G QUANTUM METHOD
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v31i3.285545Keywords:
DFT; electrophilic; electrostatic potential; Global reactivity indices; phosphate units; nucleophilic.Abstract
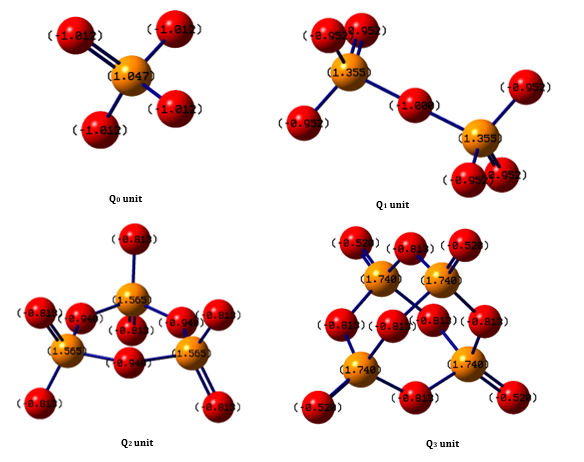
The phosphate units have been theoretically investigated through density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Ionization potential (I), electron affinity (A), electrophilicity index (ω), chemical potential (μ), hardness (ŋ), softness (S), and dipole moment (P) have been optimized. The obtained results revealed that the [PO4]3- (Q0) units act as electron donors, while the [P4O10]0 (Q3) unit acts as an electron acceptor. The passage from one unit to the other implies an increase in the number of bridging oxygens (BO) consistent with the variation of Mulliken charges. Moreover, the analysis of the optimized contours of the electrostatic potential has indicated that the electrophilic attack is more expected on the P-O-P bonds. The infrared and Raman spectra have been also predicted and the change of symmetric and asymmetric vibrational bands of the phosphate units with the number of bridging oxygens has been investigated.
References
Chen, Y., Liu, X. Y., Chen, G. H., Yang, T., Yuan, C. L., Zhou, C. R., Xu, J. W. (2017). Up-conversion luminescence and temperature sensing characteristics of Er3+/Yb3+ co-doped phosphate glasses, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 28(20), 15657–15662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7454-9
Canioni, L., Bellec, M., Royon, A., Bousquet, B., Cardinal, T. (2008). Three-dimensional optical data storage using third-harmonic generation in silver zinc phosphate glass. Opt. Lett., 33(4), 360–362. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.33.000360
Das, S.S., Baranwal, B.P., Gupta, C.P., Singh, P. (2003). Characteristics of solid-state batteries with zinc/cadmium halide-doped silver phosphate glasses as electrolytes. J. Power Sources, 114(2), 346–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(02)00604-3
Juárez-Batalla, J., Meza-Rocha, A. N., Camarillo, I., Caldiño, U. (2016). Luminescence properties of Tb3+-doped zinc phosphate glasses for green laser application. Opt., 58, 406–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2016.06.022
Zachariasen, W. H. (1932) The atomic arrangement in glass. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 54(10), 3841–3851. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01349a006
Brow, R. K., (2000) Review: the structure of simple phosphate glasses, J. Non- Cryst. Solids, 263–264, 1–28
Hoppe, U. (1996) A structural model for phosphate glasses, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 195(12), 138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(99)00620-1
Abe, Y., Hayashi, M., Iwamoto, T., Sumi, H., Hench, L. (2005). Superprotonic conducting phosphate glasses containing water, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 351(2426) 2138–2141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2005.05.010
Broer, M. M., Bruce, A. J., Grodkiewicz, W. H. (1992). Photoinduced refractive-index changes in several Eu3+-, Pr3+-, and Er3+-doped oxide glasses, Phys. Rev. B, 45(13) 7077–7083. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.45.7077
Lee, C., Yang, W., Parr, R. G. (1988). Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B, 37(2) 785. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.37.785
Frisch M.J., Trucks G.W., Schlegel H.B., Scuseria G.E., Robb M.A., Cheeseman J.R. (2009). Gaussian 09 revision C, 1. Gaussian Inc, Wallingford C.T.
Stewart, J. J. (1989). Optimization of parameters for semi empirical methods II. Applications. J. Comput. Chem., 10(2), 221–264.
Parr, R. G., Yang, W. (1989). Density-functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules, Oxford University Press, New York, Oxford.
Khan, M. F., Rashid, R. B., Rahman, M. M., Al Faruk, M., Rahman, M. M., Rashid, M. A. (2017). Effects of solvent polarity on solvation free energy, dipole moment, polarizability, hyperpolarizability and molecular reactivity of aspirin. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci, 9(2), 217–221. doi: 10.22159/ijpps.2017v9i2.15853
Vijayakumar, S., Kolandaivel, P. (2006). Study of static dipole polarizabilities, dipole moments, and chemical hardness for linear CH3–(CC) n–X (X= H, F, Cl, Br, and NO2 and n= 1–4) molecules. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM. 770(1-3), 23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theochem.2006.04.030
Afzal, Q. Q., Jaffar, K., Ans, M., Rafique, J., Iqbal, J., Shehzad, R. A., Mahr, M. S. (2022). Designing benzothiadiazole based highly efficient non-fullerene acceptor molecules for organic solar cells. Polymer, 238, 124405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2021.124405
Politzer, P.; Murray, J. S. (2004). Molecular Electrostatic Potentials; Taylor & Francis Group, LLC: New York, NY, USA.
Mathammal, R.; Sangeetha, K.; Sangeetha, M.; Mekala, R.; Gadheeja, S. (2016). Molecular structure, vibrational, UV, NMR, HOMOLUMO MEP, NLO, NBO analysis of 3, 5 di tert butyl 4 hydroxy benzoic acid. J. Mol. Struct., 1120, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.05.008
Boufas, W.; Dupont, N.; Berredjem, M.; Berrezag, K.; Becheker, I.; Berredjem, H.; Aouf, N.-E. (2014). Synthesis and antibacterial activity of sulfonamides. SAR and DFT studies. J. Mol. Struct., 1074, 180–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.05.066
Ebenso, E. E., Arslan, T., Kandemi̇rlı, F., Love, I., Öğretır, C., Saracoğlu, M., & Umoren, S. A. (2010). Theoretical studies of some sulphonamides as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acidic medium. Int. J. Quantum. Chem., 110(14), 2614–2636.
Rezania, J., Behzadi, H., Shockravi, A., Ehsani, M., Akbarzadeh, E. (2018) Synthesis and DFT calculations of some 2-aminothiazoles, J. Mol. Struct, 1157, 300–305.
Pandey, U.; Srivastava, M.; Singh, R.; Yadav, R. (2014). DFT study of conformational and vibrational characteristics of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl) benzothiazole molecule. Spectrochim. Acta Part A, 129, 61–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.12.072
Saout, G. L., Fayon, F., Bessada, C., Simon, P., Blion, A., Vaills, Y. (2001) A multispectroscopic study of PbOxZnO0.6−x(P2O5)0.4 glasses, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 293–295, 657–662.
Brow, R. K. (2000) Review: The structure of simple phosphate glasses, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 263, 1–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3093(99)00620-1
Schwarz, J., Tichá, H., Tichýa, L., Mertens, R. (2004). Physical properties of PbO-ZnO-P2O5 glasses. I. Infrared and Raman spectra, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater., 6, 737–746.
Guo, H. W., Wang, X. F., Gong, Y. X. (2010). Mixed alkali effect in xK2O-(30-x)Na2O-30P2O5-40ZnO glasses, J. Non Cryst Solids, 356, 2109–2113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2010.07.060
Ternane, R., Ferid, M., Guyot, Y. (2008). Spectroscopic properties of Yb3C in NaYbP2O7 diphosphate single crystals. J. Alloys Comp., 464, 327–331
Mandlule, A., Döhler, F., van Wüllen, L., Kasuga, T., Brauer, D. S. (2014). Changes in structure and thermal properties with phosphate content of ternary calcium sodium phosphate glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solid, 392, 31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2014.04.002
Abid, M., Et-tabirou, M., Hafid M. (2001). Glass forming region, ionic conductivity and infrared spectroscopy of vitreous sodium lead mixed phosphates. Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 407–421.
Betthet, P., Bretey, E., Berthon, J., d'Yvoire, F., Belkebir, A., Rulmont, А., Gilbert, В. (1994). Structure and ion transport properties of Na2O-Ga2O3-P2O5 glasses. Solid State Ion., 70, 476–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2738(94)90357-3
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Oles Honchar Dnipro National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

