RHEOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF ENGOBE COATINGS FOR CERAMIC BRICKS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v32i3.301951Keywords:
ceramic brick; engobe; suspension; sedimentation; fluidity; dispersion.Abstract
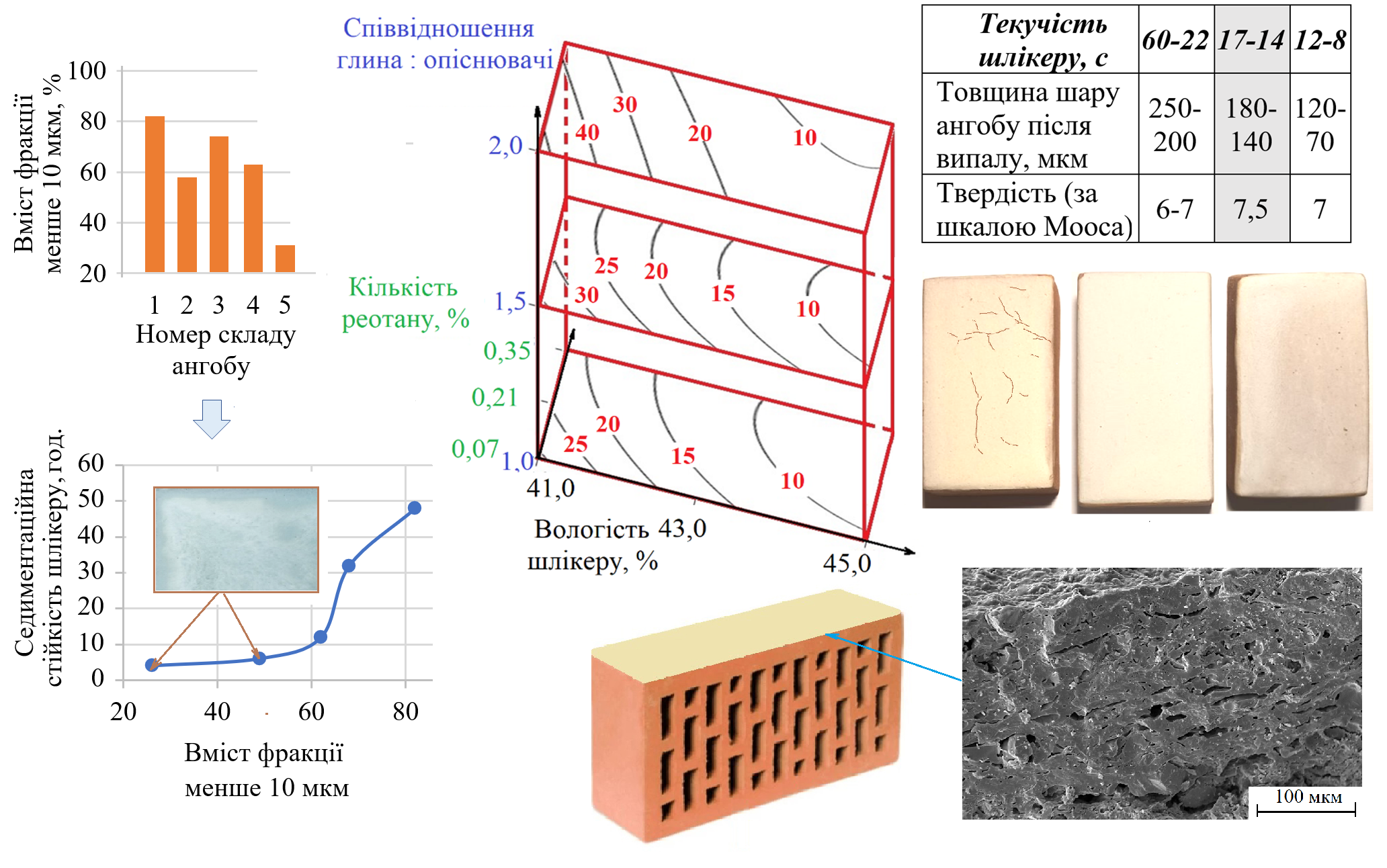
This work discusses the rheological features of engobe coatings for ceramic brick. With the correct choice of rheological parameters, the engobe coating is well matched to the ceramic base andallows to improve the aesthetic and operational properties of the brick. The requirements for the rheological parameters of engobe suspensions are formulated. This will help to avoid such defects as cracking and chipping of the coating, exposure of the product surface, formation of craters and specks. The influence of the mineralogical and particle size distribution of suspensions on their sedimentation resistance has been determined. The suspensions containing at least 70 wt.% of particles up to 10 µm have high sedimentation resistance. At the same time, the content of fractions with a size of 10-60 µm can reach up to 30 wt% without signs of suspension stratification. These can be achieved with a clay content of at least 65 wt%. A graphical model has been developed that reflects the simultaneous effect of clay, water and deflocculant (rheotane) on the fluidity of engobe suspensions. This model allows egulate the rheology of engobe suspensions when one or more factors change. To achieve a fluidity engobe suspension containing 65 wt% clay, its moisture content should be 43-43.5 wt% and the amount of rheotane should be 0.21 wt%. With such parameters, the suspension has high sedimentation resistance, a fluidity of 14-17 s, good coating ability and high adhesive strength of the coating. After firing, a coating with a thickness of 140-180 microns, with a Mohs hardness of more than 7, and no signs of any defects, was obtained on the surface of ceramic brick samples. The research results can be applied to the development of engobes and glazes in the production of ceramic bricks and tiles.
References
Cai, J., Lv, N., Jia, X., Zhang, R., Xu, G., Cai, L., Tian, Q. (2021). Properties of permeable ceramic brick prepared with felsite tailing. Journal of Building Engineering, 44, 103426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103426
Кhomenko, O. S., Sribniak, N. M., Hretsai, S. O., Teliushchenko I. F., Ivchenko, V. D., Dushyn, V. V. (2019). Development of a complex burnable additive for manufacture of porous building ceramics with high strength. Voprosy Khimii i Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii, 3, 166–175. https://doi.org/10.32434/0321-4095-2019-124-3-166-175
El-Didamony, H., El-Fadaly, E., Amer, A. A., Abazeed, I. H. (2020). [Synthesis and characterization of low cost nanosilica from sodium silicate solution and their applications in ceramic engobes]. Boletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 59(1), 31–43. (In Spanish) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bsecv.2019.06.004
da Silva Dassoler, T., de Sousa Cordeiro, E., Hotza, D., De Noni Junior, A. (2023). Photocatalytic activity of ceramic tiles coated with titania supported on kaolinite. Open Ceramics, 13, 100331 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceram.2023.100331
Khomenko, O., Datsenko, B., Sribniak, N., Nahornyi, M., Tsyhanenko, L. (2019) Development of engobe coatings based on alkaline kaolins. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 6(6-102), 49–56. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.188126
Janus, M., Zając, K. (2019) Self-cleaning efficiency of nanoparticles applied on facade bricks. Nanotechnology in Eco-efficient Construction. Materials, Processes and Applications. Woodhead Publishing Series in Civil and Structural Engineering, 591–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102641-0.00024-4
Zaichuk, A. V., Amelina, A. A. (2018). Blue-green ceramic pigments in the system CaO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2–CoO–Cr2O3 based on granulated blast-furnace slag. Voprosy Khimii i Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii, 6, 120–124. https://doi.org/10.32434/0321-4095-2018-121-6-120-124
Zaichuk, A. V., Belyi, Y. I. (2013). Improvement of the compositions and properties of gray ceramic pigments. Glass and Ceramics, 70(5-6), 229–233.
Barnat-Hunek, D., Smarzewski, P. (2015) Increased water repellence of ceramic buildings by hydrophobisation using high concentration of organic solvents. Energy and Buildings, 103, 249–260 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.06.048
Barnat-Hunek, D., Smarzewski, P., Suchorab, Z. (2016). Effect of hydrophobisation on durability related properties of ceramic brick. Construction and Building Materials, 111, 275–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.078
Soulios, V., de Place Hansen, E. J., Feng, C. Janssen, H. (2020). Hygric behavior of hydrophobized brick and mortar samples. Building and Environment, 176, 106843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.106843
Tarannum, N., Pooja, Km., Khan, R. (2020) Preparation and applications of hydrophobic multicomponent based redispersible polymer powder: A review. Construction and Building Materials, 247, 118579 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118579
Li, T., Fan, Y., Wang, K., Song, S., Liu, X., Bu, N., Li, R., Zhen, Q., Bashir, S. (2021). Methyl-modified silica hybrid fluorinated Paraloid B-72 as hydrophobic coatings for the conservation of ancient bricks. Construction and Building Materials, 299, 123906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.12390
Esposito Corcione, C., Striani, R., Frigione, M. (2014.) Novel hydrophobic free-solvent UV-cured hybrid organic–inorganic methacrylic-based coatings for porous stones. Progress in Organic Coatings, 77, 4, 803–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2014.01.008
Jaramillo Nieves, L. J., Nastri, S., Lot, A. V., Melchiades, F. G., Marsola, G. A., Flauzino, I. S., Innocentini, M. D. M., Boschi, A. O. (2022) Influence of engobe and glaze layers on the evolution of porosity and permeability of single-fired porcelain tiles. Applied Clay Science, 228, 106635 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106635
Dal Bó, M., Bernardin, A. M., Hotza, D. (2014). Formulation of ceramic engobes with recycled glass using mixture design. Journal of Cleaner Production, 69, 243–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.01.088
Bao, Z., Wang, S., Miao, L., Xu, Y., Cheng, Z., Wang, X. (2024). Preparation, properties and formation mechanism of transparent anorthite-based glass-ceramic glaze with high hardness. Ceramics International, 50(14), 26182–26192 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.04.359
Hosseiny, A. H. M., Najafi, A., Khalaj, G. (2024). Investigation of CaO/MgO on the formation of Anorthite, Diopside, Wollastonite and Gehlenite phases in the fabrication of fast firing ceramic tiles. Construction and Building Materials, 394, 132022 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132022
Peterson, M., Bernardin A. M., Kuhnen N. C., Riella H. G. (2007). Evaluation of the steger method in the determination of ceramic-glaze joining. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 466(1–2), 183–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.02.046
Khomenko, O., Sribniak, N., Dushyn, V., Shushkevych, V. (2018). Analysis of the interaction between properties and microstructure of construction ceramics. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4/6(94), 16–25. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2018.140571
Nestertsov, A. I. (2004). Underglaze engobe for ceramic facing tiles. Glass Ceram, 61, 413–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-005-0015-3
Samoilenko, N., Shchukina, L., Baranova, A. (2019). Development of engobe composition with the use of pharmaceutical glass waste for glazed ceramic granite. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4/10(100), 6–12. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.175922
Tarhan, M., Tarhan, B. (2020). Development of waterproof engobe layer for ceramic wall tiles. J Therm Anal Calorim, 140, 555–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08893-3
Nandi, V. S., Raupp-Pereira, F., Montedo, O. R. K., Oliveira, A. P. N. (2015). The use of ceramic sludge and recycled glass to obtain engobes for manufacturing ceramic tiles. Journal of Cleaner Production, 86, 461–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.08.091
Muge, T., Baran, Т. (2020). Development of waterproof engobe layer for ceramic wall tiles. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 140(2), 555–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08893-3
Kizinievič, O., Gencel, O., Kizinievič, V., Sutcu, M., Skamat, J. (2023). Recycling of dolomite powder in clay bricks: Effects on characteristics and gas release. Construction and Building Materials, 404, 133217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133217
Izzo, F., Ciotola, A., Guarino, V., Verde, M., De Bonis, A., Germinario, C., Capaldi, C., Morra, V. (2023). Focusing on red and black engobes in Roman pottery from Cumae (southern Italy): Pompeian Red Ware and Graue Platten ceramic productions. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 47, 103778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2022.103778
Sánchez-Soto, P. J., Garzón, E., Pérez-Villarejo, L., Eliche-Quesada, D. (2023). Sintering behaviour of a clay containing pyrophyllite, sericite and kaolinite as ceramic raw materials: Looking for the optimum firing conditionsSinterización de una arcilla que contiene pirofilita, sericita y caolinita como materia prima cerámica: buscando las condiciones óptimas de cocción. Boletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 62(1), 26–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bsecv.2021.09.001
Barreto I. A. R., Lima da Costa M. (2018). Sintering of red ceramics from yellow Amazonian latosols incorporated with illitic and gibbsitic clay. Applied Clay Science, 152, 124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.11.003
Martínez-Martínez, S., Pérez-Villarejo, L., Garzón, E., Sánchez-Soto, P. J. (2023). Influence of firing temperature on the ceramic properties of illite-chlorite-calcitic clays. Ceramics International, 49(14), B, 24541–24557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.11.077
Nieves, L. J. J., Nastri, S., Lot, A. V. (2022). Influence of engobe and glaze layers on the evolution of porosity and permeability of single-fired porcelain tiles. Applied Clay Science, 228, 106635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106635
Gol, F., Yilmaz, A., Kacar, E., Simsek, S., Sarıtas, Z. G., Ture, C., Arslan, M., Bekmezci, M., Burhan, H., Sen, F. (2021). Reuse of glass waste in the manufacture of ceramic tableware glazes. Ceramics International, 47(15), 21061–21068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.108
Kalirajan, M., Ranjeeth, R., Vinothan, R., Vidyavathy, S. M., Srinivasan, N.R. (2016). Influence of glass wastes on the microstructural evolution and crystallization kinetics of glass-ceramic glaze. Ceramics International, 42(16), 18724–18731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.09.011
Khomenko, O.S., Datsenko, B.M., Fomenko, G.V. (2023). [Study of clay raw materials for clinker brick production]. Voprosy khimii i khimicheskoi tekhnologii, 5, 135–146. (in Ukrainian) http://dx.doi.org/10.32434/0321-4095-2023-150-5-135-146
Samoilenko, N., Shchukina, L. (2019). Development of engobe composition with the use of pharmaceutical glass waste for glazed ceramic granite. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 4/10(100). 6–12. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2019.175922
Khomenko, O., Tsyhanenko, L., Tsyhanenko, H., Borodai, A., Borodai, D., Borodai, S. (2023). Designing engobe coatings for ceramic bricks. Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies, 3(6), 77–87. https://doi.org/10.15587/1729-4061.2023.279918
Surovtcev, A. B., Polyvianyi, A. M., Tokarev, V. S., D'yachenko, M. P., Shevchuk, O. M., Tokarev, S. V. (2018). The effect of surface modification of particulate kcl filler on rheological behaviour of its paste-like composites. Journal of Chemistry and Technologies, 26(1). https://doi.org/10.15421/08172601
Farmani, Z., Dijksman, J. A. (2024). Rate dependence in adhesive particle–particle contacts affect ceramic suspension bulk flow behavior. Powder Technology, 434, 119353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2023.119353
Bao, Z., Huan, D., Yu, H., Wang, Y., Chang, Q. (2024). A model for predicting the stability of ceramic suspensions. Ceramics International, 50(1, B), 1990–1999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.10.305
Allard, J., Burgers, S., González, M. C. R., Zhu, Y., De Feyter, S., Koos, E. (2022). Effects of particle roughness on the rheology and structure of capillary suspensions. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 648, 129224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129224
Gürgen, S., Li, W., Kuşhan, M. C. (2016). The rheology of shear thickening fluids with various ceramic particle additives. Materials & Design, 104, 312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.05.055
Lin, L., Wu, H., Huang, Z., Wu, S. (2022). Effect of monomers with different functionalities on stability, rheology, and curing behavior of ceramic suspensions. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 275, 125243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125243
Izak, P., Ogłaza, L., Mozgawa, W., Mastalska-Popławska, J., Stempkowska, A. (2018). Influence of the type of aqueous sodium silicate on the stabilization and rheology of kaolin clay suspensions. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 196, 155–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2018.02.022
Esfahani, H. B., Yekta, B. E., Marghussian, V.K. (2012). Rheology and gelation behavior of gel-cast cordierite-based glass suspensions. Ceramics International, 38(2), 1175–1179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.08.046
Zhang, X., Du, H., Gong, X., Hu, X., Zhang, D. (2014). The importance of surface hydration and particle shape on the rheological property of silica-based suspensions. Ceramics International, 40(4), 5473–5480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.10.135
Khomenko, E. S., Karasik, E. V., Goleus, V. I. (2017). Impact of kaolin addition on properties of quartz ceramics. Functional Materials, 24(4), 593–598. https://doi.org/10.15407/fm24.04.593
Leiva, W., Ayala, L., Robles, P., Nieto, S., Castellón, C., Herrera, N., Jeldres, R. (2024). Sodium acid pyrophosphate as a rheological modifier of clay-based tailings in saline water. Applied Clay Science, 253, 107352 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2024.107352
Evcin, A. (2011). Investigation the Effects of Different Deflocculants on the Viscosity of Slips. Scientific Research and Essays, 6(11), 2302–2305. http://www.academicjournals.org/SRE
Dikmen, S., Mucur, T., Arsoy, Z., Ersoy, B. (2020). The Relationship between the Flow Properties of Clay Slurry Samples and the Properties of Ceramic Green/Sintered Products. European Journal of Science and Technology, 20, 233–247. https://doi.org/10.31590/ejosat.752832
Li, J., Liang, J., Wang, F., Wang, L. (2015). Effect of sepiolite fibers addition on sintering behavior of sanitary bodies. Applied Clay Science, 105–106, 231–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2014.10.017
Soares, L., Dal-Bó, A. G., Bernardin, A. M. (2021) Use of enameling wastewater in the wet milling process for ‘monoporosa’ tile composition. Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 5, 100338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2021.100338
Willenbacher, N., Georgieva, K. (2013). Rheology of disperse systems. Product design and engineering: Formulation of gels and pastes, 7–49. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527654741.ch1
Krishnaiah, K., Shahabudeen, P. (2012). Applied design of experiments and taguchi methods. PHI Learning.
Kim, H., Kim, T. Measurement of hardness on traditional ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 22(9–10), 1437–1445. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-2219(01)00457-5
Houivet, D., Bernard, J. (2021). Powder Mixing and Grinding Processes for Ceramics. Encyclopedia of Materials: Technical Ceramics and Glasses, 1, 112–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818542-1.00109-0
Delaqua, G. C. G., Vernilli, Jr. F., Teixeira, S. R., Colorado, H. A. L., Monteiro, S. N., Vieira, C. M. F. (2023). Influence of glass particle size on the physico-mechanical properties of red ceramic. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 26, 6942–6954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.09.040
Tan, X., Liu, F., Hu, L., Reed, A. H., Furukawa, Y., Zhang, G. (2017). Evaluation of the particle sizes of four clay minerals. Applied Clay Science, 135, 313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.10.012
Essam, A., Mostafa, S. A., Khan, M., Tahwia, A. M. (2023). Modified particle packing approach for optimizing waste marble powder as a cement substitute in high-performance concrete. Construction and Building Materials, 409, 133845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133845
Kočí, J., Maděra, J., Jerman, M., Černý, R. (2015). Computational assessment of thermal performance of contemporary ceramic blocks with complex internal geometry in building envelopes. Energy and Buildings, 99, 61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.04.017
Castellini, E., Berthold, C., Malferrari, D., Bernini, F. (2013) Sodium hexametaphosphate interaction with 2:1 clay minerals illite and montmorillonite. Applied Clay Science, 83–84, 162–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2013.08.031
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Oles Honchar Dnipro National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

