SYNTHESIS OF SILVER NANOPARTICLES AND THEIR CONJUGATE WITH CEFTRIAXONE USING CHAENOMELES JAPONICA, CHARACTERIZATION, AND ACTIVITY AGAINST STAPHYLOCOCCUS EPIDERMIDIS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v33i1.311700Keywords:
green synthesis, AgNPs, UV-Vis, FTIR, SEM, SERS, bacterial resistance, ceftriaxone-conjugated nanoparticlesAbstract
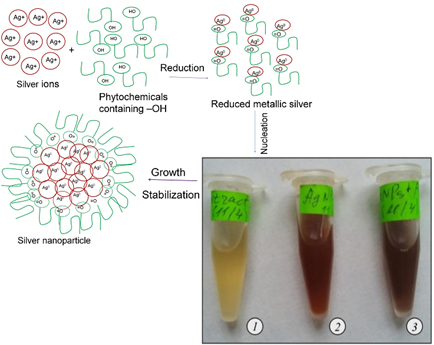
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) synthesized on the base of biological matrices are being actively studied, especially as antimicrobial agents against resistant pathogens. The paper reports the biosynthesis of AgNPs using Chaenomeles japonica aqueous leaf extract. Production of Ch-AgNPs and ceftriaxone-conjugated Ch-AgNPs-Cfx was confirmed by UV-Vis spectroscopy with the surface Plasmon resonance peaks at 472 and 475 nm respectively. SEM micrographs showed the fabricated AgNPs with a round, nearly spherical shape, and an average size of 30 – 35 nm. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy designated the involvement of hydroxyl and carboxyl functional groups of phenolics, flavonoids, terpenoids, alcohols, and carboxylic acids from Ch. japonica extract into bioreduction process of Ag+ to Ag0, and participation of protein carbonyl and amine groups in the capping and stabilization of AgNPs, as well as the binding of β-lactam ring of ceftriaxone with Ch-AgNPs-Cfx. Raman spectroscopy of Ch-AgNPs detected the significant SERS effect for Rhodamine 6G registered at 10-7 M, which confirmed the suitability of phytosynthesized AgNPs as the effective substrates in development of new biosensors. Antibacterial activity of Ch-AgNPs and Ch-AgNPs-Cfx against Staphylococcus epidermidis clinical strain, resistant to several common cephalosporins, was dose-dependent (in the range 2.5–20.0 μg/disc) in the absence of ceftriaxone antibacterial activity, indicating the potential ability of both biosynthesized nanomaterials to overcome the antibiotic resistance of St. epidermidis. Further research is needed to confirm the applicability of Ch-AgNPs and Ch-AgNPs-Cfx for development the new antibacterial drugs against the resistant bacterial strains.
References
Hajfathalian, M., Mossburg, K.J., Radaic, A., Woo, K.E., Jonnalagadda, P., Kapila, Y., Bollyky, P.L., Cormode, D.P. (2024). A review of recent advances in the use of complex metal nanostructures for biomedical applications from diagnosis to treatment. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol., 16, e1959. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1959
Dzhagan, V., Smirnov, O., Kovalenko, M., Mazur, N., Hreshchuk, O., Taran, N., Plokhovska, S., Pirko, Y., Yemets, A., Yukhymchuk, V., Zahn, D.R.T. (2022). Spectroscopic Study of Phytosynthesized Ag Nanoparticles and Their Activity as SERS Substrate. Chemosensors, 10(4), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10040129
Smirnov, O., Dzhagan, V., Kovalenko, M., Gudymenko, O., Dzhagan, V., Mazur, N., Isaieva, O., Maksimenko, Z., Kondratenko, S., Skoryk, M., Yukhymchuk, V. (2023). ZnO and Ag NPs-decorated ZnO nanoflowers: green synthesis using Ganoderma lucidum aqueous extract and characterization. RSC Advances, 13(1), 756–763. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA05834K
Mihailović, V., Srećković, N., Nedić, Z.P., Dimitrijević, S., Matić, M., Obradović, A., Selaković, D., Rosić, G., Katanić Stanković, J.S. (2023). Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Salvia verticillata and Filipendula ulmaria Extracts: Optimization of Synthesis, Biological Activities, and Catalytic Properties. Molecules, 28(2), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020808
Tizeta Abera. (2020). Review on Biosynthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles. IJMSA, 9(3), 47–52. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijmsa.20200903.12
Selvaraj, R., Ramesh, V., Thivaharan, V. (2017). Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Calliandra haematocephala leaf extract, their antibacterial activity and hydrogen peroxide sensing capability. Arab. J. Chem., 10(2), 253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.06.023
Hassan, M. H. A., Ismail, M.A., Moharram, A.M., Shoreit, A. (2016). Synergistic effect of Biogenic Silver-nanoparticles with β lactam Cefotaxime against Resistant Staphylococcus arlettae AUMC b-163 isolated from T3A Pharmaceutical Cleanroom, Assiut, Egypt. Am J Microbiol Res., 4(5), 132–137. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajmr-4-5-1
Borovaya M., Horiunova I., Plokhovska S., Pushkarova N., Blume Y., Yemets A. (2021). Synthesis, properties and bioimaging applications of silver-based quantum dots. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 22(22), 12202. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212202.
Smirnov, O., Dzhagan, V., Yeshchenko, O., Kovalenko, M., Vuichyk, M., Dzhagan, V., Mazur, N., Skoryk, M., Yukhymchuk, V. (2023). Effect of pH of Ganoderma lucidum aqueous extract on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci.: Nanosci. Nanotech., 14(3), 035009. https://doi.org/10.1088/2043-6262/acebd4.
Ewunkem, A.J., Williams, Z.J., Johnson, N.S., Brittany, J.L., Maselugbo, A., Nowlin, K. (2023). Exploring the “Carpenter” as a substrate for green synthesis: Biosynthesis and antimicrobial potential. GPD, 2(4), 2155. https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.2155
Osman, A.I., Zhang, Y., Farghali, M., Rashwan, A.K., Eltaweil, A. S., El‑Monaem, E.M.A., Mohamed, I.M.A., Badr, M.M., Ihara, I., Rooney, D.W., Yap, P-S. (2024). Synthesis of green nanoparticles for energy, biomedical, environmental, agricultural, and food applications: A review. Environ Chem Lett., 22, 841–887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-023-01682-3
Čuk, N., Šala, M., Gorjanc, M. (2021). Development of antibacterial and UV protective cotton fabrics using plant food waste and alien invasive plant extracts as reducing agents for the in-situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Cellulose, 28, 3215–3233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03715-y
Akhter, S., Rahman, A., Ripon, R.K., Mubarak, M., Akter, M., Mahbub, S., Al Mamun, F., Sikder, T. (2024). A systematic review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plants extract and their bio-medical applications. Heliyon, 10(11), e29766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29766
Raj, S., Mali, S.C., Trivedi, R. (2018). Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Enicostemma axillare (Lam.) leaf extract. BBRC, 503(4), 2814–2819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.045
Singh, J., Dutta, T., Kim, K.-H., Rawat, M., Samddar, P., Kumar, P. (2018). “Green” synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: applications for environmental remediation. J Nanobiotechnol., 16(84), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0408-4
Hossain, M.M., Polash, S.A., Takikawa, M., Shubhra, R.D., Saha, T., Islam, Z., Hossain, S., Hasan, M.A., Takeoka, S., Sarker, S.R. (2019). Investigation of the Antibacterial Activity and in vivo Cytotoxicity of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles as Potent Therapeutics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 7, 239. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2019.00239
Hemmati, S., Rashtiani, A., Zangeneh, M.M., Mohammad, P., Zangeneh, A., Veisi, H. (2019). Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Fritillaria flower extract and their antibacterial activity against some human pathogens. Polyhedron, 158, 8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2018.10.049
Al-Zahrani, S. A., Bhat, R. S., Al Rashed, S. A., Mahmood, A., Al Fahad, A., Alamro, G., Almusallam, J., Al Subki, R., Orfali, R., Al Daihan, S. (2021). Green-synthesized silver nanoparticles with aqueous extract of green algae Chaetomorpha ligustica and its anticancer potential. Green Process. Synth., 10(1), 711–721. https://doi.org/10.1515/gps-2021-0067
Ren, Y-Y., Yang, H., Wang, T., Wang, C. (2019). Bio-synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity. Mater. Chem. Phys., 235, 121746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.121746
Yin, I.X., Zhang, J., Zhao, I.S., Mei, M.L., Li, Q., Chu, C.H. (2020). The antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and its application in dentistry. Int. J. Nanomed, 15, 2555–2562. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S246764
Reddy, N.V., Li, H., Hou, T., Bethu, M.S., Ren, Z., Zhang, Z. (2021). Phytosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Perilla frutescens Leaf Extract: Characterization and Evaluation of Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activities. Int J Nanomedicine, 16, 15–29. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S265003
Mubeen B., Ansar A.N., Rasool R., Ullah I., Imam S.S., Alshehri S., Ghoneim M.M., Alzarea S.I., Nadeem M.S., Imran Kazmi I. (2021). Nanotechnology as a novel approach in combating microbes providing an alternative to antibiotics. Antibiotics, 10(12), 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121473
Adil, M., Alam, S., Amin, U., Ullah, I., Muhammad, M., Ullah, M., Rehman, A., Khan, T. (2023). Efficient green silver nanoparticles-antibiotic combinations against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. AMB Express, 13, 115. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-023-01619-7
Ghai, I. (2024). Electrophysiological Insights into Antibiotic Translocation and Resistance: The Impact of Outer Membrane Proteins. Membranes, 14(7), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390%2Fmembranes14070161
Panáček, A., Smékalová, M., Večeřová, R., Bogdanová, K., Röderová, M., Kolář, M., Kilianová, M., Hradilová, S., Froning, J.P., Havrdová, M., Prucek, R., Zbořil, R., Kvítek, K. (2016). Silver nanoparticles strongly enhance and restore bactericidal activity of inactive antibiotics against multiresistant Enterobacteriaceae. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 142, 392–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.03.007
Smekalova, M., Aragon, V., Panacek, A., Prucek, R., Zboril, R., Kvitek, L. (2016). Enhanced antibacterial effect of antibiotics in combination with silver nanoparticles against animal pathogens. Vet J, 209, 174–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.10.032
Sánchez-López, E., Gomes, D., Esteruelas, G., Bonilla, L., Lopez-Machado, A.L., Galindo, R., Cano, A., Espina, M., Ettcheto, M., Camins, A., Silva, A.M., Durazzo, A., Santini, A., Garcia, M.L., Souto, E.B. (2020). Metal-based nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: An overview. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020292.
Qing, Y., Cheng, L., Li, R., Liu, G., Zhang, Y., Tang, X., Wang, J., Liu, H., Qin, Y. (2018). Potential antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and the optimization of orthopedic implants by advanced modification technologies. Int. J. Nanomed., 13, 3311–3327. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S165125
Vazquez-Muñoz, R., Meza-Villezcas, A., Fournier, P., Soria-Castro, E., Juarez-Moreno, K., Gallego-Hernández, A., Bogdanchikova, N., Vazquez-Duhalt, R., Huerta-Saquero, A. (2019). Enhancement of antibiotics antimicrobial activity due to the silver nanoparticles impact on the cell membrane. PLoS ONE 14(11), e0224904. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0224904
Cook, M.A., Wright, G.D. (2022). The past, present, and future of antibiotics. Sci. Transl. Med., 14 (657), eabo7793. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abo7793
Yuan, P., Ding, X., Yang, Y.Y., Xu, Q.H. (2018). Metal Nanoparticles for Diagnosis and Therapy of Bacterial Infection. Adv. Healthc. Mater., 7(13), 1701392. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201701392
Feizi, S., Cooksley, C.M., Nepal, R., Psaltis, A.J., Wormald, P.-J., Vreugde, S. (2022). Silver nanoparticles as a bioadjuvant of antibiotics against biofilm-mediated infections with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Pathology, 54(4), 453–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pathol.2021.08.014
Adil M., Khan, T., Aasim, M., Khan, A.A., Ashraf, M. (2019). Evaluation of the antibacterial potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized through the interaction of antibiotic and aqueous callus extract of Fagonia indica. AMB Express, 9, 75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0797-2
Langer, J., Jimenez de Aberasturi, D., Aizpurua, J., Alvarez-Puebla, R.A., Auguié, B., et al. (2020). Present and Future of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. ACS Nano, 14(1), 28–117. https://doi.org/10.1021%2Facsnano.9b04224
Karan, T., Gonulalan, Z., Erenler, R., Kolemen, U., Eminagaoglu, O. (2024). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Sambucus ebulus leaves extract: Characterization, quantitative analysis of bioactive molecules, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. J. Mol. Struct., 1296(1), 136836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.136836
Khromykh, N.O., Lykholat, Y.V., Shupranova, L.V., Kabar, A.M., Didur, O.O., Kulbachko, U.L. (2018). Interspecific differences of antioxidant ability of introduced Chaenomeles species with respect to adaptation to the steppe zone conditions. Biosyst. Divers., 26(2), 132–138. https://doi.org/10.1542/011821
Lykholat, Y.V., Khromykh, N.O., Didur, O.O., Drehval, O.A., Sklyar, T.V., Anishchenko, A.O. (2021). Chaenomeles speciosa fruit endophytic fungi isolation and characterization of their antimicrobial activity and the secondary metabolites composition. BJBAS, 10, 83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-021-00171-2
EUCAST Disk Diffusion Method for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing – Version 5.0 (January 2015). http://www.eucast.org/
Das, P., Ashraf, G.J., Baishya, T., Dua, T.K., Paul, P., Nandi, G., Dutta, A., Limbu, D., Kumar, A., Adhikari, M.D., Dewanjee, S., Sahu, R. (2024). Formulation of silver nanoparticles using Duabanga grandiflora leaf extract and evaluation of their versatile therapeutic applications. Bioproc Biosyst Eng., 47, 1139–1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-024-02975-9
Al-Rajhi A.M.H., Salem S.S., Alharbi A.A., Abdelghany T.M. (2022). Ecofriendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Kei-apple (Dovyalis caffra) fruit and their efficacy against cancer cells and clinical pathogenic microorganisms. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 15(7), 103927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.103927
Kargar, P.G., Shafiei, M., Bagherzade, G. (2024). Transformation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural to 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furan carboxylic acid mediated by silver nanoparticles biosynthesized from Spartium junceum flower extract. Mater Today Sustain., 25, 100622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtsust.2023.100622
Amina, M., Al Musayeib, N.M., Alarfaj, N.A., El-Tohamy, M.F., Al-Hamoud, G.A. (2020). Antibacterial and Immunomodulatory Potentials of Biosynthesized Ag, Au, Ag-Au Bimetallic Alloy Nanoparticles Using the Asparagus racemosus Root Extract. Nanomaterials, 10, 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122453
Singh, P., Mijakovic, I. (2022). Rowan Berries: A Potential Source for Green Synthesis of Extremely Monodisperse Gold and Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Property. Pharmaceutics, 14(1), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010082
Bagherzade, G., Tavakoli, M.M., Namaei, M.N. (2017). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) wastages and its antibacterial activity against six bacteria. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed., 7(3), 227–233. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2016.12.014
Banaei, N., Foley, A., Houghton J.M., Sun Y., Kim, B. (2017). Multiplex detection of pancreatic cancer biomarkers using a SERS-based immunoassay. Nanotechnology, 28(45), 455101. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aa8e8c
Asante, J., Hetsa, B.A., Amoako, D.G., Abia, A.L.K., Bester, L.A., Essack, S.Y. (2021). Genomic Analysis of Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolates from Clinical Sources in the Kwazulu-Natal Province, South Africa. Front. Microbiol., 12, 656306. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.656306.
Xu, Z., Misra, R., Jamrozy, D., Paterson, G. K., Cutler, R. R., Holmes, M. A., Gharbia, S., Mkrtchyan, H.V. (2018). Whole genome sequence and comparative genomics analysis of multi-drug resistant environmental Staphylococcus epidermidis ST59. G3 Genes Genomes Genet., 8(7), 2225–2230. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.118.200314.
U Din, M.M., Batool, A., Ashraf, R.S., Yaqub, A., Rashid, A., U Din, N.M. (2024). Green Synthesis and Characterization of Biologically Synthesized and Antibiotic-Conjugated Silver Nanoparticles followed by Post-Synthesis Assessment for Antibacterial and Antioxidant Applications. ACS Omega, 9(17), 18909–18921.https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.3c08927
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oles Honchar Dnipro National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

