EFFECT OF SYNTHESIS TIME ON THE MORPHOLOGY OF MONODISPERSE SILICA MICROSPHERES
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v32i4.315165Keywords:
silica, sol-gel, porous structure, mesopores, dendritic nanoparticles, synthesisAbstract
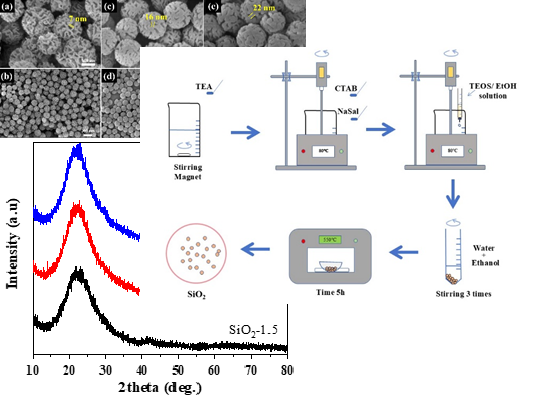
Silica (SiO2) microspheres can be used in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, food, coating and other technological applications. Consequently, the task is to search for optimal parameters for easy synthesis of monodisperse silica microspheres with controlled structural and physicochemical characteristics. The aim was to study the effect of synthesis time on the formation of silica microspheres for control of their surface morphological properties. The synthesis was conducted by alkaline hydrolysis in an aqueous/alcohol solution using structure-directing agents, namely cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and sodium salicylate (NaSal), in conjunction with an inorganic precursor, namely tetraethoxysilane (TEOS). The synthesis time varied from 1.5 to 5 hours. The following methods were used to study the synthesised silica microspheres: X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and low-temperature N2 adsorption/desorption method. As a result were synthesized silica spheres with a consistent diameter of approximately 200 nm and mesoporous structure, regardless of synthesis duration. However, the thickness of the nanosheets forming the sphere structure increased from 7 nm to 22 nm as the synthesis time extended. The sample synthesised for 1.5 hours showed the highest specific surface area, reaching 504 m²/g.
References
Kurbanov, M., Tulaganov, S., Nuraliev, U., Andriyko, L., Goncharuk, O., Guzenko, N., Nychyporuk, Yu., Marynin, A. (2023). Comparative characteristics of the structure and physicochemical properties of silica synthesized by pyrogenic and fluoride methods. Silicon, 15, 1221–1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-022-02087-7
Yu, J., Bondarieva, A., Tobilko, V., Pavlenko, V. (2023). Adsorption removal of Cu(II) using Ni-modified silica gel. Water and Water Purification Technologies. Scientific and Technical News, 37(3), 3–12. https://doi.org/10.20535/2218-930032023302423
Szczęśniak, B., Choma, J., Jaroniec, M. (2020). Major advances in the development of ordered mesoporous materials. Chemical Communications, 56, 7836–7848. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CC02840A
Usman, P., Duru, I.A., Akalezi, C.O., Njoku, C., Kovo, A., Oguzie, E.E. (2024). Mesoporous silica-based smart nanocontainers for corrosion inhibition: a mini-review. Journal of Coatings Technology and Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-024-00942-3
Zhang, S., Bai, J., Kong, W., Song, H., Liu, Yu., Liu, G., Ma, Li., Zhou, L., Jiang, Y. (2024). Dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enzyme immobilization. Green Chemical Engineering, 5(2), 173–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gce.2023.07.002
Polshettiwar, V. (2022). Dendritic fibrous nanosilica: discovery, synthesis, formation mechanism, catalysis, and CO2 capture-concersion. Accounts of Chemical Research, 55(10), 1395–1410. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00031
Sharma, K., Hooda, A., Goyat, M.S., Rai, R., Mittal, A. (2022). A review on challenges, recent progress and applications of silica nanoparticles based superhydrophobic coatingds. Ceramic International, 48(5), 5922–5938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.11.239
Stöber, W., Fink, A., Bohn, E. (1968). Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 26(1), 62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(68)90272-5
Kresge, C.T., Roth, W.J. (2013). The discovery of mesoporous molecular sieves from the twenty year perspective. Chemical Society Reviews, 42(9), 3663–3670. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CS60016E
Rahmat, N., Abdullah, A., Mohamed, A. (2010). A review: mesoporous Santa Barbara Amorphous-15, types, synthesis and its applications towards biorefinery production. American Journal of Applied Sciences, 7(12), 1579–1586. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajassp.2010.1579.1586
Polshettiwar, V., Cha, D., Zhang, X., Basset, J.M. (2010). High-surface-area silica nanospheres (KCC-1) with a fibrous morphology. Angewandte Chemie, 49(50), 9652–9656. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201003451
Wang, X.-D., Shen, Z.-X., Sang, T., Cheng, X.-B., Li, M.-F., Chen, L.-Y., Wang, Z.-S. (2010). Preparation of spherical silica particles by Stöber process with high concentration of tetra-ethyl-orthosilicate. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 341(1), 23-29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.09.018
Lee, K., Sathyagal, A.N., McCormick, A.V. (1998). A closer look at an aggregation model of the Stöber process. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 144(1-3), 115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-7757(98)00566-4
Sivolapov, P., Myronyuk, O., Baklan, D. (2022). Synthesis of Stober silica nanoparticles in solvent environments with different Hansen solubility parameters. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 143, 109769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109769
Chen, Q., Larismaa, J., Keski-Honkola, A., Vilonen, K., Söderberg, O., Hannula, S.-P. (2012). Effect of synthesis time on morphology of hollow porous silica microspheres. Materials Science, 18(1), 66–71. http://dx.doi.org/10.5755/j01.ms.18.1.1344
Feng, J., Liu, Y., Liu Ch., Hu, W., Zhang, Ch., Li, S., Song, Y., Yu, Ch. (2020). The impact of ethanol and chlorobenzene in the structure regulation of dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 307, 110504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110504
Wang, Yu., Song, H., Yang, Y., Liu, Y., Tang, J., Yu, Ch. (2018). Kinetically controlled dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles: from dahlia- to pomegranate-like structures by micelle filling. Chemistry of Materials, 30(16), 5770–5776. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b02712
Yu, J., Tobilko, V. (2024). Adsorption removal of copper(II) from water by zero valent iron loaded dendritic mesoporous silica. Technology Audit and Production Reserves, 5(3(79), 6–12. https://doi.org/10.15587/2706-5448.2024.314231
Zhang, K., Xu, L.-L., Jiang, J.-G., Calin, N., Lam, K.-F., Zhang, S.-J., Wu, H.-H., Wu, G.-D., Albela, B., Bonneviot, L., Wu, P. (2013). Facile large-scale synthesis of monodisperse mesoporous silica nanospheres with tunable pore structure. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 135(7), 2427–2430. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja3116873
Gao, F., Lei, Ch., Liu, Y., Song, H., Kong, Y., Wan, J., Yu, C. (2021). Rational design of dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles’ surface chemistry for quantum dot enrichment and an ultrasensitive lateral flow immunoassay. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13(18), 21507–21515. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c02149
Innocenzi, P., Falcaro, P., Grosso, D., Babonneau, F. (2003). Order-disorder transitions and evolution of silica structure in self-assembled mesostructured silica films studied through FTIR spectroscopy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 107(20), 4711–4717. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp026609z
Lei, Z., Pang, X., Li, Na, Lin, L., Li, Y. (2009). A novel two-step modifying process for preparation of chitosan-coated Fe3O4/SiO2 microspheres. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 209(7), 3218–3225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.07.044
Dong, K., Wu, S., Chang, B., Sun, T. (2023). Zero-valent iron supported by dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles to purify dye wastewater. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 11(5), 110434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.110434
Li, H., Si, R., Wang, W., Huang, Y., Xiang, M., Wang, C., Chen, S., Cao, W., Lu, Z., Huang, M. (2021). Sulfidated nanoscale zero-valent iron dispersed in dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres for degrading tetrabromobisphenol A. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 621, 126586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126586
Yang, Y., Bernardi, S., Song, H., Zhang, J., Yu, M., Reid, J.C., Strounina, E., Searles, D.J., Yu, C. (2016). Anion assisted synthesis of large pore hollow dendritic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles: understanding the composition gradient. Chemistry of Materials, 28(3), 704–707. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b03963
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oles Honchar Dnipro National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

