POTENTIOMETRIC SENSOR FOR THE DETERMINATION OF ZYPROSIDONE BASED ON ITS ION ASSOCIATE WITH EOSIN
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v32i4.316467Keywords:
potentiometric sensor, ziprosidone, ionic associate, eosinAbstract
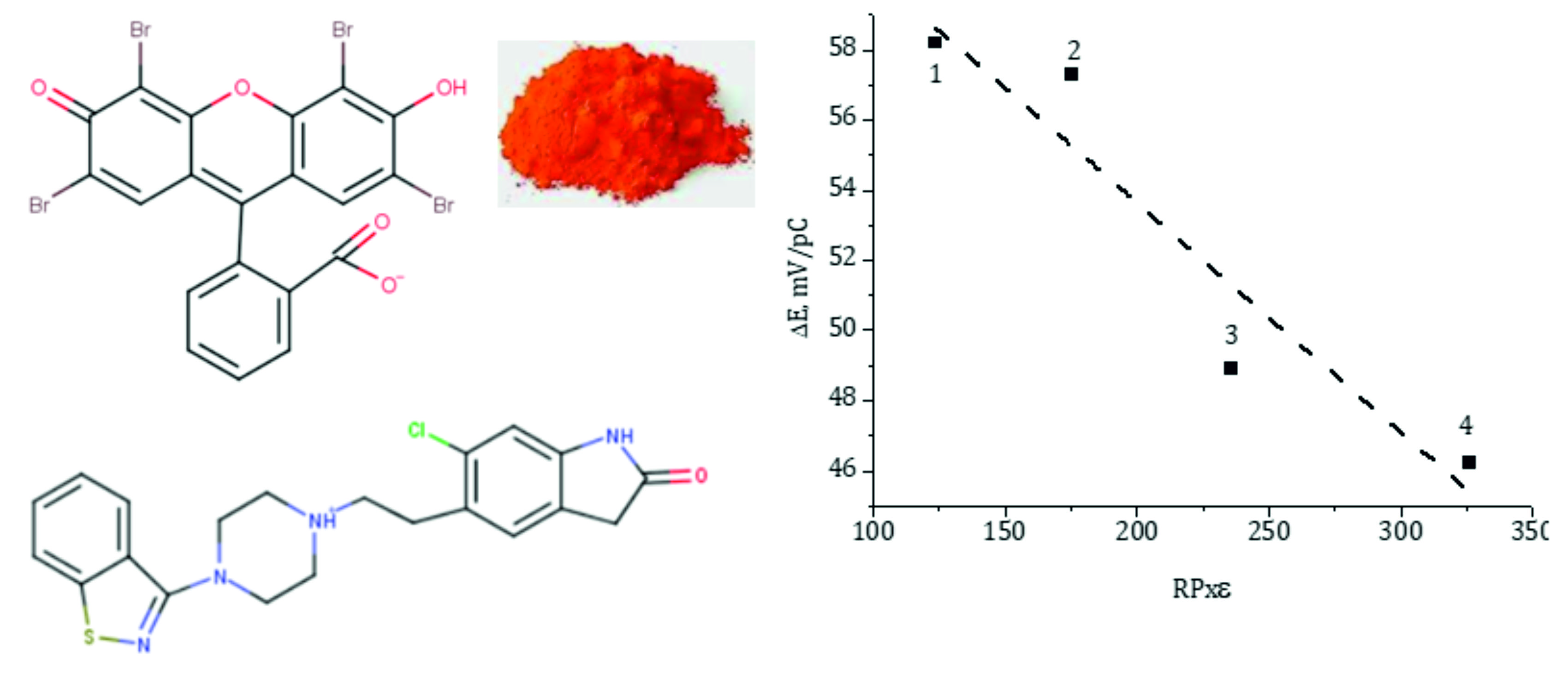
The energy efficiency of the formation of the ionic associate (IA) of zyprosidone with eosin was substantiated by the quantum chemical method. It is shown that the difference between the energy of formation of IA and the sum of the energy of formation of its components is equal to 110.2 kJ/mol. Therefore, the process of its formation is thermodynamically advantageous. The formation conditions were substantiated and IA was synthesized, which was used as an electroactive substance to create a ziprosidone selective sensor. For membranes plasticized with phthalates, the steepness of the electrode function is closer to the theoretical value for singly charged ions with the content of the plasticizer in the membrane with the lowest dielectric constant – dinonyl phthalate (DNР). As the dielectric constant of the plasticizer in the membrane increases, the angular coefficient of the electrode function of the sensor decreases. To characterize the plasticizers, the product of the dielectric constant of the solvent and the Rorschneider polarity (ε × PR) is proposed. The dependence of the slope of the sensor electrode function on this parameter is observed not only within the homologous series of phthalic acid esters, but also of other plasticizers, in particular, tricresyl phosphate (TCF). Moreover, solvents with a lower value of this parameter - TСР and DNР – turned out to be more effective. For the best sensor, the operating pH range is observed in the range from 3.5 to 5.5, the slope of the electrode function is 58.2 mV/рС. The linearity of the electrode function and the lower limit of detection are 5·10-5–1·10-3 and 5·10-5 mol/l Zypr, respectively. The electrode potential is established in 10–12 s and is stable for at least six weeks. The technique of potentiometric determination of zyprosidone in medicinal forms has been developed.
References
Baldassano, C.F., Ballas, C., Datto, S.M., Kim, D., Littman, L., O'Reardon, J., Rynn, M.A. (2003). Ziprasidone-associated mania: a case series and review of the mechanism. Bipolar Disord., 5(1), 72–75. doi:10.1034/j.1399-5618.2003.02258.x.
Farde, L., Wiesel, F.A., Halldin, C., Sedvall, G. (1988). Central D2-dopamine receptor occupancy in schizophrenic patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry., 45, 71–76. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1988.01800250087012.
Mamo, D., Kapur, S., Shammi, C.M., Papatheodorou, G., Mann, S., Therrien, F., Remington, G. (2004). A PET study of dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT2 receptor occupancy in patients with schizophrenia treated with therapeutic doses of ziprasidone. Am. J. Psychiatry., 161, 818–825. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.161.5.818.
Baumann, P., Hiemke, C., Ulrich, S., Eckermann, G., Gaertner, I., Gerlach, M., Kuss, H.J., Laux, G., Müller-Oerlinghausen, B., Rao, M.L., Riederer, P., Zernig, G. (2004). Arbeitsge-meinschaft fur neuropsycho-pharmakologie und pharmakopsychiatrie. The AGNP-TDM expert group consensus guidelines: therapeutic drug monitoring in psychiatry. Pharmacopsychiatry. 37(6), 243–265. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-832687.
Baumann, P., Hiemke, C., Ulrich, S., Gaertner, I., Rao, M.L., Eckermann, G., Gerlach, M., Kuss, H.J., Laux, G., Müller-Oerlinghausen, B., Riederer, P., Zernig, G. (2004). Therapeutic monitoring of psychotropic drugs: an outline of the AGNP-TDM expert group consensus guideline. Ther. Drug Monit., 26(2),167–170. doi: 10.1097/00007691-200404000-00014.
Vogel, F., Gansmuller, R., Leiblein, T., Dietmaier, O., Wassmuth, H., Grunder, G., Hiemke, C. (2009). The use of ziprasidone in clinical practice: Analysis of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic aspects from data of a drug monitoring survey. European Psychiatry, 24, 143–148. doi:10.1016/j.eurpsy.2008.09.003.
Ayano, G. (2016). Second Generation Antipsychotics: Pharmacodynamics, Therapeutic Effects Indications and Associated Metabolic Side Effects: Review of Articles. J. Schizophr. Res., 3(2): id1027. 01–05.
Farah, A. (2005). Atypicality of atypical antipsychotics. Prim Care Companion J. Clin. Psychiatry. 7 (6), 268–74. doi:10.4088/pcc.v07n0602.
Srinubabu, G., Rani, B., Rao, J.S. (2006). Spectrophotometric determination of Ziprasidone in pharmaceutical formulations. E-J. Chem., 3, 9–12. doi:10.1155/2006/643624.
Chauhan, C., Choudhury, P. (2010). UV spectrophotometric determination of ziprasidone hydrochloride in pore and pharmaceutical formulation. Asian J. Chem., 19(1), 819–820.
Mahale, M.V., Todkari, V.B., Kangane, M.R., Mohite, S.K., Magdum, C.S., Hembade, M.J. (2013). U.V. spectrophotometric method development for quantitative estimation of Ziprasidone hydrochloride. Intern. J. Pharm. Arch., 2(5), 92–94.
Mathrusri Annapurna, M., Malavika, V. (2022). New spectrophotometric methods for the estimation of Ziprasidone - An Antipsychotic drug. Res. J. Pharm. Techn., 15(7), 3209–3202. doi: 10.52711/0974-360X.2022.00538.
Choudhary, P.K., Sharma, P.K., Mathur, A.K., Ramnani, P., Jain, P. (2005). Development and validation of spectrophotometric method for the estimation of Ziprasidone HCl. Orient. J. Chem., 21(1).
Vijayalakshmi, R., Kalyani, K., Padma, J., Pushpamadhavi, M., Dhanaraju, M.D. (2010). Simple spectrophotometric methods for the determination of ziprasidone hydrochloride in pharmaceuticals using Folin-Ciocalteau and potassium ferricyanide. Orient. J. Chem., 26(2), 713–715.
El-Sherif, Z.A., El-Zeany, B., El-Houssini, O.M., Rashed, M.S., Aboul-Enein, H.Y. (2004). Stability indicating reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic and thin layer densitometric methods for the determination of ziprasidone in bulk powder and in pharmaceutical formulations. Biomed. Chromatogr., 18, 143–149. doi: 10.1002/bmc.299.
Aniszewski, J.S., Fouda, H.G., Cole, R.O. (1995). Development and validation of a high-sensitivity assay for an antipsychotic agent, CP-88,059, with solid-phase extraction and narrow-bore highperformance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B, 668, 133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4347(95)00071-P.
Suckow, R.F., Fein, M., Correll, C.U., Cooper, T.B. (2004). Determination of ziprasidone using liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B, 799, 201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2003.10.027.
Sachse, J., Haertter, S., Hiemke, C. (2005). Automated determination of ziprasidone by HPLC with column switching and spectrophotometric detection. Ther. Drug Monit., 27, 158–162. doi: 10.1097/01.ftd.0000150879.36296.4d.
Aldirbashi, O., Aboul-Enein, H., Alodaib, A., Jacob, M., Rashed, M. (2006). Rapid liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for quantification of ziprasidone in human plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr., 20, 365–368. doi: 10.1002/bmc.571.
Aravagiri, M., Marder, S., Pollock, B. (2007). Determination of ziprasidone in human plasma by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry and its application to plasma level determination in schizophrenia patients. J. Chromatogr. B., 847, 237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.10.024.
Farin, C., Kremser, L., Raggi, M., Kenndler, E. (2008). Determination of ziprasidone in pharmaceutical formulations by capillary zone electrophoresis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 46, 471–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2007.11.01
Kul, D., Gumustas, M., Uslu, B., Ozkan, S.A. (2010). Electroanalytical characteristics of antipsychotic drug ziprasidone and its determination in pharmaceuticals and serum samples on solid electrodes. Talanta, 82, 286–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.04.036.
AL-Timimi Zahra. (2019). A comparative study of determination the spectral characteristics of serum total protein among laser system and spectrophotometric: advantage and limitation of suggested methods. Curr. Analyt. Chem. 15(5), 583–590. doi: 10.2174/1573411014666180531092053.
Isildak, Ö., Özbek, O. (2020). Application of potentiometric sensors in real samples. Critical Rev. Analyt. Chem., 51(3), 218–231. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2019.1711013.
Kormosh, Z., Khalavka, Y., Susheel K. Mittal. (2023). Design and application of potentiometric sensors for the determination of mefenamic and phenylanthranilic acids. Anal. Methods. 15, 1903–1914. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2AY02092K.
Kormosh, Z., Gorbatyuk, N., Kormosh, N., Shevchuk, M., Liushuk, K., Kotsar, V., Bokhan, Yu., Borkova, S. (2023). Novel Potentiometric Sensor for the Determination of Ibuprofen. Pharm. Chem. J. 57(5), 745–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-023-02946-6.
Kormosh, Z., Susheel K. Mittal, Tkach, V., Yurchenko, O. (2022). Ionic associates of fuchsine basic dye as sensing probe for potentiometric determination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxy- and 4-chlorophenoxy acetic acids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 9(4). 373–380. doi: 10.22036/ABCR.2022.292168.1649.
Kormosh, Zh., Kormosh, N., Golub, S., Pachenko, Yu., Yurchenko, O., Savchuk, T., Korolchuk, S., Borkova, S., Suprunovich, S. (2022). New potentiometric sensor for determination of metformin. Pharm. Chem. J. 56(8), 1140–1143; doi 10.1007/s11094-022-02765-1.
Kormosh, Zh., Kormosh, N., Bokhan, Y., Horbatiuk, N., Yurchenko, O., Tkach, V., Onyschuk, O. (2022). The new mephenaminate- and phenylanthranilate-selective membrane sensor. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 14(1), 32–44.
Kormosh, Zh., Matskiv, O., Kormosh, N., Forostovska, T., Bokhan, Y., Golub, V., Gorbatyuk, N., Karaim, O. (2022). Potentiometric sensor for ketoprofen determination. Pharm. Chem. J. 55(12), 1412–1415. doi 10.1007/s11094-022-02590-6.
Kormosh, Zh., Kormosh, N., Bokhan, Yu., Gorbatyuk, N., Kotsan, I., Suprunovich, S., Parchenko, V., Savchuk, T., Korolchuk, S. Potentiometric Sensor for Naproxen Determination. (2021). Pharm. Chem. J. 55(1), 97–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-021-02379-z.
Zareh M.M. (2012). Plasticizers and their role in membrane selective electrodes. Recent Advances in Plasticizers. doi: 10.5772/36620.
Pechenkina, I.A., Mikhelson, K.N. (2015). Materials for the ionophore-based membranes for ion-selective electrodes: Problems and achievements (review paper). Russ. J. Electrochem. 51, 93–102. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1023193515020111.
Soledad García, M., Ortuño, J. A., Cuartero, M., Abuherba, M.S. (2011). Use of a new ziprasidone-selective electrode in mixed solvents and its application in the analysis of pharmaceuticals and biological fluids. Sensors. 11. 8813–8825. doi:10.3390/s110908813.
Kormosh, Z.A., Matviichuk, O.Y., Antal, I.P. Basel, Y.R. (2020). Sensors based on single- and double-layer plasticized membranes for the potentiometric determination of mefenamic and phenylanthranylic acids. J. Anal. Chem., 75, 820–828. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934820060131.
Sakač, N., Madunić-Čačić, D., Karnaš, M., Đurin, B., Kovač, I., Jozanović, M. (2021). The influence of plasticizers on the response characteristics of the surfactant sensor for cationic surfactant determination in disinfectants and antiseptics. Sensors, 21, 3535. 1–12. doi: 10.3390/s21103535.
Mchedlov-Petrossyan, N.O. (2004). [Fluorescein dyes in solutions: well studied systems?]. Kharkov University Bulletin. №626. Chemical Series, 11(34), 221–312. (in Russian).
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Oles Honchar Dnipro National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

