INCREASING THE ELECTROCHEMICAL ACTIVITY OF NICKEL-BASED ELECTRODE MATERIALS BY CORROSION TREATMENT
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v32i4.317362Keywords:
corrosion treatment, nickel foil, nickel sulfides, sodium sulfide, oxygen electroreductionAbstract
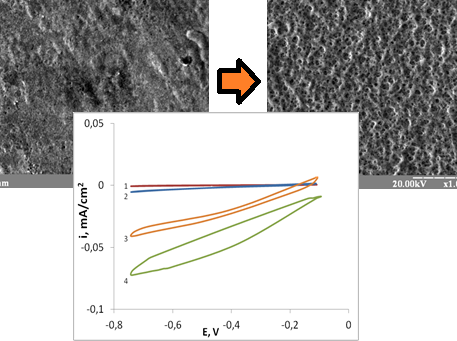
Recent studies have extensively explored the catalytic properties and synthesis of chalcogenide materials, with a particular focus on sulfides of iron-group metals. Of particular interest are nickel sulfides, in particular those that correspond in stoichiometry to natural millerite and hizlewudite. These chalcogenide compounds have garnered significant attention due to their high electrical conductivity, comparable to pure nickel, and their remarkable catalytic performance in oxygen electroreduction. Cyclic voltammetry measurements reveal that prolonging the corrosion treatment of bright sulfur-containing nickel coatings in concentrated acetic acid increases the sulfur content on the surface, leading to enhanced current densities in the cyclic voltammetry curves. Similarly, the elevated current densities observed for sulfur-free nickel coatings are linked to prolonged exposure in a saturated sodium sulfide solution. Regardless of the processing method, the presence of nickel sulfides or adsorbed sulfur enhances the electrochemical activity of the electrode material. Thus it has been shown, for the first time, that in both cases, during corrosion treatment of bright nickel deposits and during adsorption treatment of matte nickel in a sodium sulfide solution, stabilization of the cathodic current density value occurs after 24 hours of both types of treatment. Accordingly, the cathodic current density, in this case, is a parameter that determines the overall electrochemical activity of the studied materials. It has been shown that the formed during corrosion treatment nickel sulfides is the most stable and effective for the electroreduction of oxygen in a low alkaline medium.
References
Huang, L., Zaman, S., Tian, X., Wang, Z., Fang, W., Xia, B.Y. (2021). Advanced Platinum-Based Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells. Accounts of Chemical Research, 54(2), 311–322 https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00488
Huang, K., Song, T., Morales-Collazo, O., Jia, H., Brennecke, J. F. (2017) Enhancing Pt/C Catalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction with Protic Ionic Liquids: The Effect of Anion Structure. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 164(13), F1448–F1459. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.1071713jes
Li, O.L., Shi, Z., Lee, H., Ishizaki, T. (2019). Enhanced Electrocatalytic Stability of Platinum Nanoparticles Supported on Sulfur-Doped Carbon using in-situ Solution Plasma. Scientific Reports, 9, 12704. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49194-x
Buchmaier, C., Glanzer, M., Torvisco, A., Poelt, P., Wewerka, K., Kunert, B., Gatterer, K., Trimmel, G., Rath, T. (2017). Nickel sulfide thin films and nanocrystals synthesized from nickel xanthate precursors. Journal of Materials Science, 52, 10898–10914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1265-5
Yao, S., Huang, T., Fang, H., Yu, J., Meganathan, M.D., Cui, Z., Yuan, X. (2020). Cobalt sulfides as efficient catalyst towards oxygen reduction reactions. Chinese Chemical Letters, 31(2), 530–534 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.04.069
Fang, H., Huang, T., Mao, J., Yao, S., Dinesh, M. M., Sun, Y., Liang, D., Qi, L., Yu, J., Jiang Z. (2018). Investigation on the Catalytic Performance of Reduced-Graphene-Oxide-Interpolated FeS2 and FeS for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Chemistry Select, 3, 10418–10427. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201800835
Wang, H.-F., Tang, C., Zhang Q. (2018). A Review of Precious-Metal-Free Bifunctional Oxygen Electrocatalysts: Rational Design and Applications in Zn−Air Batteries. Advanced Functional Materials, 1803329–1803329. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201803329
Yan, B., Concannon, N. M., Milshtein, J. D., Brushett, F. R., Surendranath Y. (2017) A Membrane-Free Neutral pH Formate Fuel Cell Enabled by a SelectiveNickel Sulfide Oxygen Reduction Catalyst. Angew. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 56, 7496. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201702578
Gahtar, A., Benramache, S., Zaouche C. (2020). Effect of temperature on the properties of nickel sulfide films performed by spray pyrolysis technique. Advances in materials science, 20(3), 36–51. https://doi.org/10.2478/adms-2020-0015
Gibbs, G. V., Downs, R. T., Prewitt, C. T., Rosso, K. M., Ross, N. L., Cox, D. F. (2005) Electron density distributions calculated for the nickel sulfides millerite, vaesite, and heazlewoodite and nickel metal: a case for the importance of ni ni bond paths for electron transport. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 109, 21788–21795 https://doi.org/10.1021/jp054109a
Yan, B., Krishnamurthy, D., Hendon, C. H., Deshpande, S., Surendranath, Y., Viswanathan, V. (2017). Surface Restructuring of Nickel Sulfide Generates Optimally Coordinated Active Sites for Oxygen Reduction Catalysis. Joule 1(3), 600–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2017.08.020.
Falkowski, J. M., Concannon, N. M., Yan, B., Surendranath, Y. (2015). Heazlewoodite, Ni3S2: A Potent Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction to Water under Benign Conditions, Journal of American Chemical Society, 137(25), 7978–7981. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b03426
Xia, Q., Si, L., Liu, K., Zhou, A., Su, C., Shinde, N.M., Fan, G., Dou, J. (2023). In Situ Preparation of Three-Dimensional Porous Nickel Sulfide as a Battery-Type Supercapacitor. Molecules, 28, 4307. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114307
Gaikar, P., Pawar, S. P., Mane, R. S., Nuashad, M., Shinde, D. V. (2016). Synthesis of nickel sulfide as a promising electrode material for pseudocapacitor application. RSC Advances, 6, 112589–112593. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA22606J
Xu, Y., Sumboja, A., Groves, A., Ashton, T., Zong, Y., Darr, J. A. (2020). Enhancing bifunctional catalytic activity of cobalt–nickel sulfide spinel nanocatalysts through transition metal doping and its application in secondary zinc–air batteries. RSC Advances, 10, 41871 https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA08363A
Ding, X., Liu, D., Zhao, P., Chen, X., Wang, H., Oropeza, F. E., Gorni, G., Barawi M., García-Tecedor, M., de la Peña O’Shea, V.A., Hofmann, J. P., Li, J., Kim, J., Cho, S., Wu R., Zhang K. H. L. (2024). Dynamic restructuring of nickel sulfides for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Nature Communication, 15, 5336 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-49015-4
Wang, S., Yuan, D., Sun, S., Huang, S., Wu, Y., Zhang, L., Dou, S. X., Liu, H. K., Dou, Y., Xu, J. (2024). Iron, Tungsten Dual-Doped Nickel Sulfide as EfficientBifunctional Catalyst for Overall Water Splitting. Small, 20, 2311770 https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202311770
Marcus, Ph. (2012). Corrosion Mechanisms in Theory and Practice, Third Edition. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, 395–416. https://doi.org/10.1201/b11020
Ushchapovskiy, D. Y., Byk, M. V., Linyucheva, O. V., Frolenkova, S. V., Red’ko, R. M., Yakubenko, V. V. (2020). Corrosion resistance of bright nickel coatings in the vapor of acetic acid. Materials Science, 55(5), 656–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-020-00356-7
Ushchapovskiy, D.Y., Liniucheva, O.V., Kushmyruk, A.I. Redko, R.M., Pidvashetskyi, H.Y. (2023). Comparative Study of Corrosion Activity of Bright and Matte Nickel Coatings in Solutions and Vapor of Acetic Acid. Materials Science, 58(4), 540–547 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-023-00696-0
Ushchapovskyi, D.Yu., Kushmyruk, A.I., Vasiliev, G.S., Linyucheva, O.V., Redko, R.M., Linyuchev, O.G., Pidvashetsky, G.Yu., Kurochenko, T.A. (2022). Corrosion resistance of galvanic nickel deposits and electrochemical activity of their corrosion products, KPI Science News, 1–2, 110–117 http://scinews.kpi.ua/article/view/253045/282527
Qiao, J., Xu, L., Ding, L., Shi, P., Zhang, L., Baker, R., Zhang, J. (2013). Effect of KOH Concentration on the Oxygen Reduction Kinetics Catalyzed by Heat-Treated Co-Pyridine/C Electrocatalysts. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 8, 1189–1208 http://www.electrochemsci.org/papers/vol8/80101189.pdf
Haynes, W.M. (Ed.). (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92th ed.). CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/b17379
Vukmirovic, M. B., Vasiljevic, N., Dimitrov, N., Sieradzki, K. (2003). Diffusion-Limited Current Density of Oxygen Reduction on Copper. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 150(1), B10–B15. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1526554
Jithul, K., Tamilarasi, B. & Pandey, J. (2024). Electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR): towards an active and stable electrocatalyst for low-temperature PEM fuel cell. Ionics 30, 6757–6787 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-024-05767-z
Payattikul, L., Chen, C. -Y., Chen, Y. -S., Raja Pugalenthi, M., Punyawudho, K. (2023). Recent Advances and Synergistic Effects of Non-Precious Carbon-Based Nanomaterials as ORR Electrocatalysts: A Review. Molecules, 28(23), 7751. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237751
Ali, A., Laaksonen, A., Huang, G. Hussain, S., Luo, S., Chen, W., Shen, P.K., Zhu, J., Ji, X. (2024). Emerging strategies and developments in oxygen reduction reaction using high-performance platinum-based electrocatalysts. Nano Research, 17, 3516–3532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6310-x
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oles Honchar Dnipro National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

