STUDY OF THE DYNAMICS OF OXIDATION OF VEGETABLE OILS TO PROLONG THE STORAGE
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v33i2.323958Keywords:
vegetable oil, peroxide number, anisidine number, oxidation, totox indexAbstract
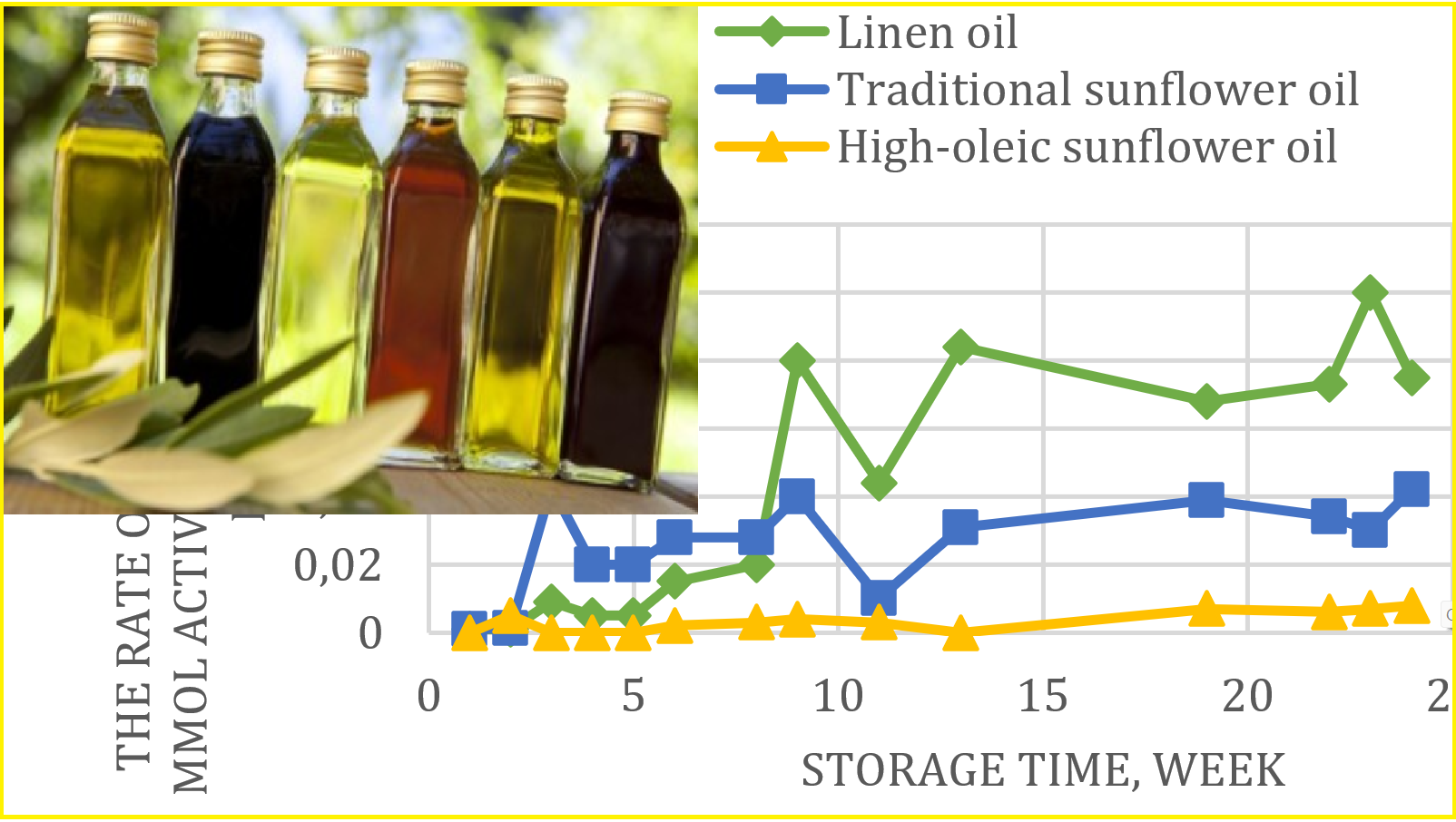
Aim. To investigate the oxidation processes of edible vegetable oils: unrefined flaxseed oil, refined high-oleic sunflower oil, and refined traditional sunflower oil. The purpose of the study was to examine and analyze the dynamics of oxidation processes in vegetable oils and their impact on the shelf life of food products containing these oils. Methods. The oxidation of oils was analyzed using the peroxide number indicator, which showed that the ratio of the average rates of peroxide compound accumulation in unrefined flaxseed oil, refined traditional sunflower oil, and refined high-oleic sunflower oil was 54 : 43 : 1, indicating a proportional relationship with their degree of unsaturation. The primary oxidation products formed in the oil are unstable, leading to the formation of new radical compounds and more stable secondary oxidation products. The study included the determination of carbonyl compounds, characterized by the anisidine number. Results. The research revealed an important feature of unrefined flaxseed oil oxidation: the anisidine number increased more rapidly compared to refined traditional and high-oleic sunflower oils. This indicates the relative instability of unrefined flaxseed oil hydroperoxides, which undergo destruction to form carbonyl and other secondary compounds. Due to its high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, unrefined flaxseed oil is vulnerable to oxidation and mixing it with refined high-oleic sunflower oil can enhance the oxidative stability of food products. Conclusions. The results highlight the importance of considering the dynamics of oxidation processes when selecting vegetable oils for food products and suggest that mixing different types of oils can improve their oxidative stability and the overall stability of food products.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oles Honchar Dnipro National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

