NEW QUATERNARY COMPOUND FeGdSbS4 IN THE FeSb2S4–FeGd2S4 SYSTEM
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v33i4.331664Keywords:
quaternary compound, crystal structure, , congruent melting, berthierite, thermal effectsAbstract
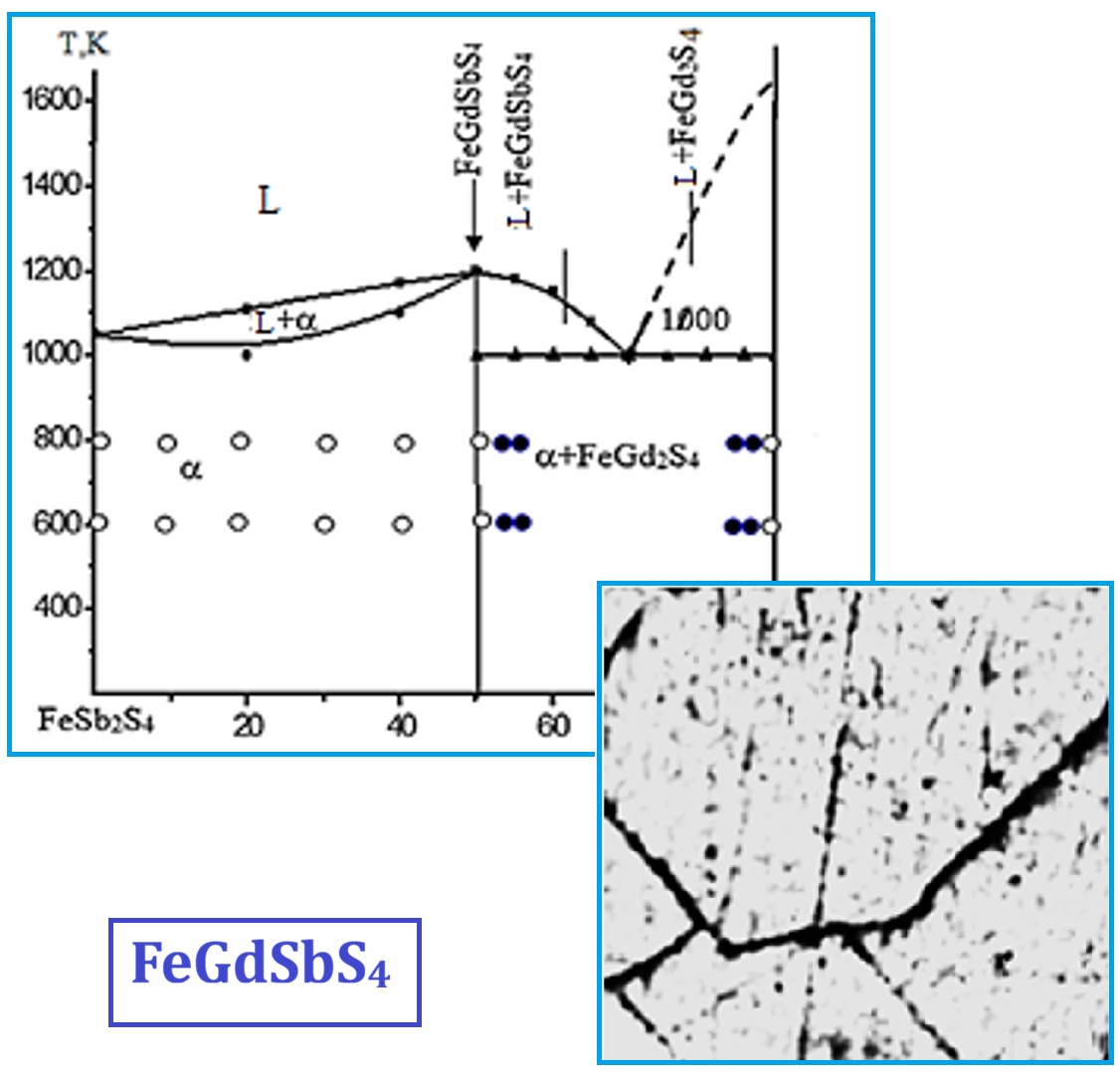
For the first time, the quaternary compound FeGdSbS₄ was studied using various physicochemical methods over a wide temperature range. The study of the FeSb₂S₄–FeGd₂S₄ system revealed that at a ratio of FeSb₂S₄:FeGd₂S₄ = 1:1, the quaternary compound FeGdSbS₄ forms. FeGdSbS₄ melts congruently at 1200 K and has a berthierite-type structure (a = 11.382, b = 13.896, c = 3.614 Å; Z = 4; V = 571.606 ų, space group Pbam). The specific electrical conductivity of FeGdSbS₄ at room temperature is 2×10⁻⁴ Om⁻¹·m⁻¹. FeGdSbS₄ is an impurity semiconductor. The thermal band gap ΔEg of FeGdSbS₄ is 1.31 eV. Investigation of the magnitude and sign of the thermoelectric power (TEP) and thermal conductivity in the FeSb₂S₄–FeGd₂S₄ system shows that both dependencies reach their maxima at the composition corresponding to FeGdSbS₄. The Seebeck coefficient (α) for FeGdSbS₄ is 1000 mkV/K, and the thermal conductivity is 1.32 Vt/m·K. The FeSb₂S₄–FeGd₂S₄ system is a quasi-binary section characterized by the formation of a quaternary compound FeGdSbS₄, which melts congruently and belongs to the berthierite structural type.
References
Peng, Q., Hu, X., Zeng, T., Shang, B., Mao, M., Jiao, X., Xi, G. (2020). FeSb2S4 anchored on amine-modified graphene towards high-performance anode material for sodium ion batteries. Chemical engineering journal, 385, 123857–123865. https://10.1016/j.cej.2019.123857
Wang, P., Ding, Y., Chu, Y., Zhu, X., Lin, J., Shao, L., Zeng, T. (2023). Nano FeSb2S4 Anchored on Exfoliated Graphite for Sodium-Ion Battery Anode via a Two-Step Fabrication. American Chemical Society, 5577–5585. https://10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c00106
Wintenberger, M., André, G. (1990). Magnetic properties and spiral magnetic structure of berthierite FeSb2S4. Physica. B, Condensed matter, 162(1), 5–12. https://10.1016/0921-4526(90)90086-A
Wintenberger, M., André, G. (1989). Magnetic structure of the mineral berthierite FeSb2S4. Physica. B, Condensed matter, 156–157, https://10.1016/0921-4526(89)90664-9
Liu, Y., Kang, C.-J., Stavitski, E., Du, Q., Petrovic, C. (2018). Polaronic transport and thermoelectricity in Fe₁-xCoₓSb₂S₄ (x=0,0.1,0.2), Phys. Rev. B 97, 155202
Anwar, A., Noor, N. A., Mustafa, G. M., Atiq, S., Ibrahim, A. & Laref, A. (2025). Mechanically robust and thermodynamically stable FeSc₂Z₄ (Z = S, Se) spinels for future spintronic architectures, RSC Advances, 15 (43), 35770–35781. DOI: 10.1039/D5RA04959H.
Furqan, M., Mustafa, G. M., Dawas Alkhaldi, H., Alhajri, F., Ameereh, G. I., Al Anazy, M. M., El Rayyes, A. Mahmood, Q. (2025). Study of the electronic, magnetic, and thermoelectric aspects of spinel chalcogenides SrCe₂Z₄ (Z = Te, Se, S) for spintronic and energy applications, RSC Advances, 15 (44), 37288–37298 DOI: 10.1039/D5RA03092G.
Noor, N. A., Tahir, M., Khan, M. A., Niaz, S., Ullah, H., Neffati, R. & Sharma, R. (2023). Theoretical study of rare earth in spinel chalcogenide MgCe₂Z₄ (Z = S, Se) for spintronic and thermo electric applications, Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 163, 107563. DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2023.107563.
Syed Awais Rouf, Hind Albalawi, Taharh Zelai, Othman Hakami, Nessrin A. Kattan, Samah Al Qaisi, Muhammad Younas, Khaild I. Hussein & Q. Mahmood. (2023). Half metallic ferromagnetism and thermoelectric effect in spinel chalcogenides SrX₂S₄ (X = Mn, Fe, Co) for spintronics and energy harvesting, Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 182, 111601. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2023.111601.
Zhang, L., Qin, B., Sun, C., Ji, Y. & Zhao, D. (2023). Effect of synthesis factors on microstructure and thermoelectric properties of FeTe₂, Materials, 16 (22), 7170 DOI: 10.3390/1996 1944/16/22/7170.
Ashiq Ramzan., Mudasir Younis Sofi., Mohammad Ishfaq ul Islam., Mohd Shahid Khan & M. Ajmal Khan. (2025). Half metallic ferromagnetism and thermoelectric efficient behavior in chalcogenide spinels MgNi₂X₄ (X = S, Se): a first principles approach, RSC Advances, 15 (29), 24002–24018. DOI: 10.1039/D5RA03555D
Mammadov, Sh. H., Gurbanov G.R., Ismailova R. A. (2025). Phase diagram of the AgGaS2–PbGa2S4 system. Voprosy Khimii i Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii, (1), 22–26. https://doi:10.32434/0321-4095-2025-158-1-22-26
Mammadov, Sh.H., Mammadov A.N., Kurbanova R.C. (2020). Quasi-Binary Section Ag2SnS3–AgSbS2. Russian Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 65(2), 217–221. https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602362001012X
Mammadov, F.M. (2020). FeS-FeGa2S4-FeGaInS4 system. Chemical Problems, 18(2), 214–221. https://doi.org/10.32737/2221-8688-2020-2-214-221
Mammadov, F. M. (2021). New version of the phase diagram of the MnTe-Ga2Te3 system. New Materials, Compounds and Applications, 5(2), 116–121. http://jomardpublishing.com/UploadFiles/Files/journals/NMCA/V5N2/MammadovF.pdf
Mammadov, Sh.H. (2020). The study of the quasi-triple system FeS-Ga2S3-Ag2S by a FeGa2S4-AgGaS2 section. Kondensirovannye Sredy Mezhfaznye Granitsy, 22(2), 232–237. https://doi.org/10.17308/kcmf.2020.22/2835
Dixit, A., Ahmed, I., Abraham, J.,El‑Bahy, Z. M. (2024). Optoelectronic and thermoelectric properties of spinel chalcogenides HgLa₂X₄ (X = S, Se): A first‑principles study, Journal of Rare Earths, 42 (10), 1927–1936. DOI: 10.1016/j.jre.2023.11.014.
Suraj, K. S., Eivari, H. A., Tatara, G. & Assadi, M. H. N. (2024). Tripling magnetite’s thermoelectric figure of merit with rare earth doping, Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 12 (36), 19212–19218. DOI: 10.1039/D4TC03153A.
Zeng, Q., Sameeullah, M., & Ali, H. (2025). DFT study of chalcogenide spinels MnSc₂X₄ (X = S, Se): structural, electronic and thermoelectric behaviour, RSC Advances, 15 (22), 9662–9675. DOI: 10.1039/D4RA08334B.
Nazir, G., Alofi, A. S., Rehman, A., Mahmood, Q., Al‑Anazy, M. & Rahman, M. F. (2024). Rare earth based Mg‑chalcogenides MgDy₂(S/Se)₄ as an emerging aspirant for spintronic and thermoelectric applications, Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 173, 108129. DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2024.108129
Koc, A., Akbulut, H., Senol, S. (2024). Investigation of structural, optical, and thermoelectric properties of ZnFe₂O₄ and Ni‑doped ZnFe₂O₄, Ceramics International, 50 (22), 45251–45262.DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.08.365.
Li, J., Xie, Y., Wang, Q., & Zhao, X. (2023). Magnetic and thermoelectric properties of rare‑earth substituted spinel ferrites: A review, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 543, 168780
Wei, Z., Deng, Y., Peng, P., Zhang, Y. & Zheng, Z. (2025). Advances in silver‑based chalcogenide flexible thermoelectric materials, CrystEngComm, 27 (8), 1055–1077 DOI: 10.1039/D4CE00915K.
Kabir, S. M., Rahman, M. T., Hossain, M. Z.R.(2024). ecent progress in chalcogenide spinels for thermoelectric applications, Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 35, 4021–4045
Patel, R., Singh, D., Kumar, V. (2024). Density functional study of structural and thermoelectric properties of chalcogenide AB₂X₄ compounds, Computational Materials Science, 221, 112552
Gao, L., Zhou, H., Chen, G. (2025). Spinel chalcogenides as multifunctional materials for energy harvesting: synthesis and properties, Progress in Materials Science, 139, 101148
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oles Honchar Dnipro National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

