XANTHAN: RESEARCH INTO INNOVATIVE MODIFICATION STRATEGIES AND INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v33i4.350021Keywords:
xanthan gum; modification; gelation; rheological properties; immobilization; biopolymer composites.Abstract
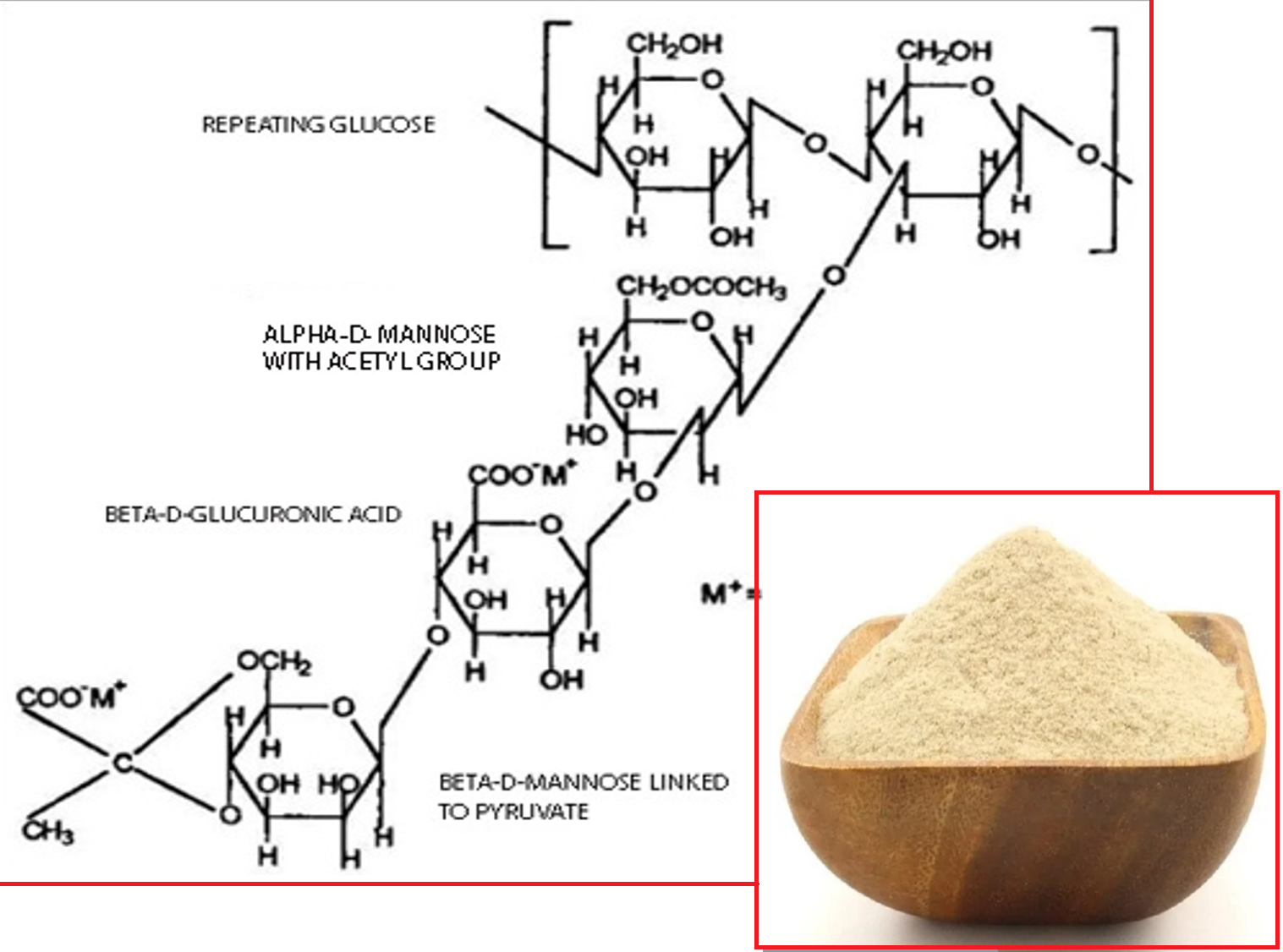
The article presents a review of current approaches to the modification of xanthan aimed at expanding its functional properties. The chemical structure of xanthan is analyzed, with particular emphasis on the organization of the main polysaccharide backbone and side chains containing carboxyl, hydroxyl, acetyl and pyruvate groups. Their key role in the formation of intermolecular interactions, gel network development, sorption capacity and the immobilization of biologically active compounds and modifying agents is demonstrated. Available data on the conditions of chemical engineering of xanthan-based systems are summarized using examples of various modification strategies, and structural features of modified gel matrices are discussed. The main application areas of xanthan in the chemical, food, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, medical, water treatment and petroleum industries are outlined, with illustrative examples of technological performance. The prospects of xanthan as a versatile platform for the development of composite materials and controlled delivery systems for active components are highlighted. The need for further research focused on the design of modified xanthan forms with predictable structure–function relationships to advance chemical engineering applications is emphasized.
References
Kumar, A., Rao, K. M., Han, S. S. (2018). Application of xanthan gum as polysaccharide in tissue engineering: A review. Carbohydrate Polymers, 180, 128–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.009
Abu Elella, M. H., Goda, E. S., Gab-Allah, M. A., Hong, S. E., Pandit, B., Lee, S., Gamal, H., Rehman, A. U., Yoon, K. R. (2021). Xanthan gum-derived materials for applications in environment and eco-friendly materials: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(1), 104702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104702
Rahmatpour, A., Alizadeh, A. H. (2024). Biofilm hydrogel derived from physical crosslinking (self-assembly) of xanthan gum and chitosan for removing Cd²⁺, Ni²⁺, and Cu²⁺ from aqueous solution. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 266(Part 2), 131394. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131394
Chemical and physical properties of xanthan gum used in cooking. (n.d.). Science of Cooking. https://www.scienceofcooking.com/chemical_physical_properties_xanthan_gum.htm
Vaishnav, A., Choudhary, D. K. (Eds.). (2021). Microbial Polymers. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0045-6
Brief introduction of xanthan gum. (2023). CD Bioparticles Blog. https://www.cd-bioparticles.net/blog/brief-introduction-of-xanthan-gum/
Buddhadev, L. (2024). A Comprehensive Review of Xanthan Gum-Based Oral Drug Delivery Systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 21, 25(18), 10143. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810143
Morris, E. R. (2019). Ordered conformation of xanthan in solutions and “weak gels”: Single helix, double helix – or both? Food Hydrocolloids, 86, 18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.11.036
Nsengiyumva, E. M., Heitz, M. P., Alexandridis, P. (2023). Thermal hysteresis phenomena in aqueous xanthan gum solutions. Food Hydrocolloids, 144, 108973.
Yahoum, M. M., Moulai-Mostefa, N., Le Cerf, D. (2016). Synthesis, physicochemical, structural and rheological characterizations of carboxymethyl xanthan derivatives. Carbohydrate Polymers, 154, 267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.080
Rakshit, P., Giri, T. K., Mukherjee, K. (2024). Research progresses on carboxymethyl xanthan gum: Review of synthesis, physicochemical properties, rheological characterization and applications in drug delivery. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 266(Part 1), 131122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131122
Vilanculos, J. R. Z., de Farias, B. S., Engelmann, J. I., Ribeiro, E. S., de Oliveira, P. D., Cadaval Jr, T. R. S., Pinto, L. A. de A. (2023). Physicochemical evaluation of chitosan–xanthan gum nanoemulsions as polyunsaturated enriched lipid–carrier. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 386, 122533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2023.122533
Ma, J., He, R., Chai, Y., Long, X., Shi, W., Chen, H., Pan, C., Zhao, Y. (2025). Stable emulsion produced by thermal modified coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) globulins-xanthan gum for protection of curcumin. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 302, 140653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140653
Yao, M., Liu, J., Liu, J., Qi, X., Bai, E., Yin, J., Wu, T. (2024). Fabrication and characterization of responsible approach for targeted intestinal releasing and enhancing the effectivity of kidney tea saponin upon porous starch /xanthan gum /sodium alginate-based hydrogel bead. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 279(Part 1), 134974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134974
Saroglu, O., Karakas, C. Y., Yildirim, R. M., Erdem, O., Karasu, S., Sagdic, O., Karadag, A. (2025). Liposomal propolis loaded xanthan gum-salep hydrogels: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro bioaccessibility of phenolics. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 300, 140323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140323
Li, Z.-X., Deng, H.-Q., Jiang, J., He, Z.-Q., Li, D.-M., Ye, X.-G., Chen, Y., Hu, Y., Huang, C. (2024). Effect of hydrothermal treatment on the rheological properties of xanthan gum. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 270(Part 2), 132229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132229
Eren, N. M., Santos, P. H. S., Campanella, O. (2015). Mechanically modified xanthan gum: Rheology and polydispersity aspects. Carbohydrate Polymers, 134, 475–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.07.092
Nsengiyumva, E. M., Heitz, M. P., Alexandridis, P. (2023). Salt and temperature effects on xanthan gum polysaccharide in aqueous solutions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(1), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25010490
Reinoso, D., Martín-Alfonso, M. J., Luckham, P. F., Martínez-Boza, F. J. (2019). Rheological characterisation of xanthan gum in brine solutions at high temperature. Carbohydrate Polymers, 203, 103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.034
Hidalgo, M. E., Armendariz, M., Wagner, J. R., Risso, P. H. (2016). Effect of xanthan gum on the rheological behavior and microstructure of sodium caseinate acid gels. Gels, 2(3), 23. doi: 10.3390/gels2030023
Nsengiyumva, E. M., Alexandridis, P. (2022). Xanthan gum in aqueous solutions: Fundamentals and applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 216, 583–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.189
Zhong, L., Oostrom, M., Truex, M. J., Vermeul, V. R., Szecsody, J. E. (2013). Rheological behavior of xanthan gum solution related to shear thinning fluid delivery for subsurface remediation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 244–245, 160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.11.028
Bak, J., Yoo, B. (2024). Rheological and tribological properties of xanthan gum-fucoidan mixture: Effect of NaCl, KCl, and CaCl₂. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 412, 125879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2024.125879
Su, L., Ji, W. K., Lan, W. Z., Dong, X. Q. (2003). Chemical modification of xanthan gum to increase dissolution rate. Carbohydrate Polymers, 53(4), 497–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(02)00287-4
Xanthan gum-modified starches (1981). Xanthan gum-modified starches. US Patent US4298729A.
Lim, S.-T., Han, J.-A., Lim, H., BeMiller, J. N. (2002). Modification of starch by dry heating with ionic gums. Cereal Chemistry, 79(5), 601–606. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM.2002.79.5.601
Zhang, C., Lim, S.-T. (2021). Physical modification of various starches by partial gelatinization and freeze-thawing with xanthan gum. Food Hydrocolloids, 111, 106210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106210
Krystyjan, M., Dobosz-Kobędza, A., Sikora, M., Baranowska, H. M. (2022). Influence of xanthan gum addition on the short- and long-term retrogradation of corn starches of various amylose content. Polymers, 14(3), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030452
Pinto, E., Furlan, L., Vendruscolo, C. (2011). Chemical deacetylation natural xanthan (Jungbunzlauer®). Polímeros, 21(1), 47–52. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0104-14282011005000005
Yahoum, M. M., Toumi, S., Tahraoui, H., Lefnaoui, S., Hadjsadok, A., Amrane, A., Kebir, M., Zhang, J., Assadi, A. A., Mouni, L. (2023). Evaluation of physicochemical and amphiphilic properties of new xanthan gum hydrophobically functionalized derivatives. Sustainability, 15(8), 6345. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086345
Hamcerencu, M., Desbrieres, J., Popa, M., Khoukh, A., Riess, G. (2007). New unsaturated derivatives of xanthan gum: Synthesis and characterization. Polymer, 48(7), 1921–1929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2007.01.048
Yang, H., Jin, L., Li, Y., Li, Q., Qu, L., Li, J. (2025). Modification study of xanthan gum to improve the suspension capacity. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Advanced Materials and Engineering Materials, 327–336. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-96-5765-0_29
Chaturvedi, S., Kulshrestha, S., Bhardwaj, K., Jangir, R. (2021). A review on properties and applications of xanthan gum. Microbial Polymers. Springer. 87–107. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-16-0045-6_4
Hamcerencu, M., Desbrieres, J., Popa, M., Riess, G. (2009). Stimuli-sensitive xanthan derivatives/N-isopropylacrylamide hydrogels: Influence of cross-linking agent on interpenetrating polymer network properties. Biomacromolecules, 10(7), 1911–1922. doi: 10.1021/bm900318g
Salehi, F., Inanloodoghouz, M. (2024). Effects of ultrasonic intensity and time on rheological properties of different concentrations of xanthan gum solution. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 263(Part 2), 130456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130456
Abou Dib, M., Gore, E., Grisel, M. (2023). Intrinsic and rheological properties of hydrophobically modified xanthan synthesized under green conditions. Food Hydrocolloids, 138, 108461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108461
Hamiouda, S., Yahoum, M. M., Lefnaoui, S., Hadjsadok, A., Moulai-Mostefa, N. (2020). New alkylated xanthan gum as amphiphilic derivatives: Synthesis, physicochemical and rheological studies. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1207, 127768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.127768
Wang, A., Zhong, Q. (2025). Properties and mechanisms of O/W emulsions stabilized by shellac and xanthan gum at acidic pH. Food Chemistry, 475, 143352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.143352
Krstonošić, V., Milanović, M., Dokić, L. (2019). Application of different techniques in the determination of xanthan gum-SDS and xanthan gum-Tween 80 interaction. Food Hydrocolloids, 87, 108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.07.040
Bak, J. H., Yoo, B. (2018). Intrinsic viscosity of binary gum mixtures with xanthan gum and guar gum: Effect of NaCl, sucrose, and pH. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 111, 77–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.144
Gago-Guillán, M., García-Otero, X., Anguiano-Igea, S., Otero-Espinar, F. J. (2023). Compression pressure-induced synergy in xanthan and locust bean gum hydrogels. Effect in drug delivery. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 89, 105025. DOI: 10.1016/j.jddst.2023.105025
Agoub, A. A., Smith, A. M., Giannouli, P., Richardson, R. K., Morris, E. R. (2007). “Melt-in-the-mouth” gels from mixtures of xanthan and konjac glucomannan under acidic conditions: A rheological and calorimetric study of the mechanism of synergistic gelation. Carbohydrate Polymers, 69(4), 713–724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.02.014
Khoobbakht, F., Khorshidi, S., Bahmanyar, F., Hosseini, S. M., Aminikhah, N., Farhoodi, M., Mirmoghtadaie, L. (2024). Modification of mechanical, rheological and structural properties of agar hydrogel using xanthan and locust bean gum. Food Hydrocolloids, 147, 109411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109411
Jadav, M., Pooja, D., Adams, D. J., Kulhari, H. (2023). Advances in xanthan gum-based systems for the delivery of therapeutic agents. Pharmaceutics, 15(2), 402. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020402
Pandey, S., Mishra, S. B. (2011). Graft copolymerization of ethylacrylate onto xanthan gum, using potassium peroxydisulfate as an initiator. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 49(4), 527–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.06.005
McClements, D. J. (2024). Composite hydrogels assembled from food-grade biopolymers: Fabrication, properties, and applications. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 332, 103278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2024.103278
Barberi, G., Biscari, G., Catania, V., Punginelli, D., Scialabba, C., Fiorica, C., Schillaci, D., Cavallaro, G. (2024). Thermosensitive and mucoadhesive xanthan gum-based hydrogel for local release of anti-Candida peptide. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 100, 106054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2024.106054
Qiao, D., Luo, M., Li, Y., Jiang, F., Zhang, B., Xie, F. (2024). Evolutions of synergistic binding between konjac glucomannan and xanthan with high pyruvate group content induced by monovalent and divalent cation concentration. Food Chemistry, 432, 137237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137237
Qiao, D., Luo, M., Li, Y., Jiang, F., Zhang, B. (2023). New evidence on synergistic binding effect of konjac glucomannan and xanthan with high pyruvate group content by atomic force microscopy. Food Hydrocolloids, 136(Part A), 108232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.108232
Fitzsimons, S. M., Tobin, J. T., Morris, E. R. (2008). Synergistic binding of konjac glucomannan to xanthan on mixing at room temperature. Food Hydrocolloids, 22(1), 36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2007.01.023
Li, M., Hou, X., Li, Y., Li, K., Qiao, D., Jiang, F., Zhu, F., Zhang, B. (2024). Konjac glucomannan and xanthan synergistic interaction gel: Underlying mechanism for improvement of gel mechanical properties induced by freeze-thaw treatment. Food Hydrocolloids, 146(Part A), 109276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109276
Grisel, M., Aguni, Y., Renou, F., Malhiac, C. (2015). Impact of fine structure of galactomannans on their interactions with xanthan: Two co-existing mechanisms to explain the synergy. Food Hydrocolloids, 51, 449–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.05.041
Lin, L., Li, K., Liu, X., Zhang, B., Zhao, G., Wu, K., Jiang, F., Qiao, D. (2024). Assembly process of locust bean gum and xanthan gum for synergistic gelling revealed by atomic force microscopy. Food Hydrocolloids, 156, 110263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2024.110263
Poret, F., Cordinier, A., Hucher, N., Grisel, M., Savary, G. (2021). Impact of the synergistic interaction between xanthan and galactomannan on the stickiness properties of residual film after application on a surface. Carbohydrate Polymers, 255, 117500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117500
Abbaszadeh, A., MacNaughtan, W., Sworn, G., Foster, T. J. (2016). New insights into xanthan synergistic interactions with konjac glucomannan: A novel interaction mechanism proposal. Carbohydrate Polymers, 144, 168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.02.026
Kurt, A., Atalar, I. (2024). Steady and dynamic shear rheology of aqueous solutions of quince seed gum combinations with locust bean or xanthan gums. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 274(Part 1), 133409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133409
Moghni, N., Hadjsadok, A. (2024). Design and characterization of alginate-xanthan based raft forming suspension for acid reflux treatment: rheological study and produced CO2 assessment. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 91, 105198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.105198
Cofelice, M., Messia, M. C., Marconi, E., Cuomo, F., Lopez, F. (2023). Effect of the xanthan gum on the rheological properties of alginate hydrogels. Food Hydrocolloids, 142, 108768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108768
Teng, Z., Huang, X., Zhang, C., Liu, X., Li, Y., Wang, C.-S., Liu, X., Xie, F. (2025). Xanthan gum modulation of octenyl succinic anhydrate starch-based high internal phase emulsions: Characterization, rheological behavior, and 3D printing applications. Food Chemistry, 464(Part 3), 141813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141813
Bhardwaj, B. Y., Vihal, S., Pahwa, R., Agarwal, S., Gupta, B., Yang, J. C., Chauhan, R., Chellappan, D. K., Gupta, G., Singh, S. K., Dua, K., Negi, P. (2025). Recent advancements in xanthan gum-based gastroretentive floating formulations: Chemical modification, production and applications. Carbohydrate Polymers, 348(Part A), 122809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.122809
Santos, T. de S., Lemos, P. V. F., Santana, J. S., Anias, F. A. S., Assis, D. de J., Cardoso, L. G., Marcelino, H. R., de Souza, E. F., da Silva, J. B. A., de Souza, C. O. (2024). Characterization of xanthan gum–metal complexes biosynthesized using a medium containing produced water and cassava processing residues. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 282 (Part 4), 137229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137229
Liu, S., Han, F., Chen, P., Zhang, R., Tao, Y. (2025). Injectable and drug-loaded gelatin methacrylate and carboxymethylated-sulfated xanthan gum hydrogels as biomimetic mineralization constructs. Carbohydrate Polymers, 355, 123354.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.123354
Han, G., Chen, Q., Liu, F., Cui, Z., Shao, H., Liu, F., Ma, A., Liao, J., Guo, B., Guo, Y., Wang, F., Ling, P., Mei, X. (2017). Low molecular weight xanthan gum for treating osteoarthritis. Carbohydrate Polymers, 164, 386–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.01.101
Wu, Q., Lu, Z., Wang, L., Peng, S., Wang, Z., Qiu, Y., Liao, Z., Wang, Y., Qin, X. (2025). Konjac glucomannan/xanthan gum hydrogels loaded with metal-phenolic networks encapsulated probiotic to promote infected wound healing. Carbohydrate Polymers, 353, 123243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.123243
Cheng, Y., Ling, J., Ouyang, X.-k., Wang, N. (2025). Curdlan/xanthan gum-based composite hydrogel with near-infrared irradiation responsive properties for infected wounds healing. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 284(Part 2), 138199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138199
Lin, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, B., Zhao, G., Guo, W., Chen, J., Jiang, F., Qiao, D. (2025). Promotion effect of the 1,2-propanediol on the gel-related properties of locust bean gum/xanthan synergistic gel system. Food Chemistry, 469, 142553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.142553
Niu, Z., Li, K., Guo, Y., Zhao, G., Wu, K., Hou, X., Qiao, D., Jiang, F., Zhang, B., Xie, F. (2024). Assembly behavior and nano-scale microstructure of tamarind gum/xanthan synergistic interaction gels. Food Hydrocolloids, 157, 110392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2024.110392
Aljewicz, M., Keklik, M., Recio, I., Martínez-Sanz, M. (2024). Effect of polysaccharide-protein interactions on the multi-scale structure of hybrid micellar casein-xanthan gum systems. Food Hydrocolloids, 151, 109833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2024.109833
Bak, J., Yoo, B. (2024). Effect of fucoidan on rheological properties of xanthan gum-guar gum mixtures. Food Bioscience, 59, 104200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104200
Wang, C. S., Virgilio, N., Carreau, P. J., Heuzey, M. C. (2021). Understanding the effect of conformational rigidity on rheological behavior and formation of polysaccharide-based hybrid hydrogels. Biomacromolecules, 22(9), 4016–4026. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.1c00803
Muhammed, N. S., Haq, M. B., Al-Shehri, D., Rahaman, M. M., Keshavarz, A., Hossain, S. M. Z. (2020). Comparative study of green and synthetic polymers for enhanced oil recovery. Polymers, 12(10), 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12102429
Zhang, Z., Sun, L., Chen, F., Liu, X., Huo, X., Pan, X., Feng, C. (2024). Host-guest strategy improves rheological properties, conformational stability and oil displacement efficiency of xanthan gum. Carbohydrate Polymers, 345, 122598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.122598
Tian, M., Fang, B., Jin, L., Lu, Y., Qiu, X., Jin, H., Li, K. (2015). Rheological and drag reduction properties of hydroxypropyl xanthan gum solutions. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 23(9), 1440–1446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2015.04.003
Cano-Barrita, P. F. de J., León-Martínez, F. M. (2016). Biopolymers with viscosity-enhancing properties for concrete. Biopolymers and Biotech Admixtures for Eco-Efficient Construction Materials. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-100214-8.00011-7
Wenbo, F., Sun, L., Xiaoming, Z., Hualong, X., Meiwen, C. (2025). Enhancing metal corrosion inhibition with xanthan gum: The synergistic role of anionic surfactants. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 711, 136364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2025.136364
Ahmadi, Y., Akbari, A., Mansouri, M., Alibak, A. H., Vaferi, B. (2024). Innovative xanthan gum-based nanocomposites for asphaltene precipitation prevention in shale and carbonate rocks. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 280(Part 1), 136331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136331
Altan Kamer, D. D., Kaynarca, G. B., Yılmaz, O. Ş., Gümüş, T. (2024). Waste to value: Enhancing xanthan gum hydrogel with wine lees extract for optimal performance. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 259(Part 2), 129342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129342.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Oles Honchar Dnipro National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

