PROCESSING OF W-Ni-Fe SCRAP TO RECEIVE TUNGSTEN POWDER
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15421/jchemtech.v32i2.302114Keywords:
powdered tungsten; binder phase; self-grinding; recycling; leaching degree.Abstract
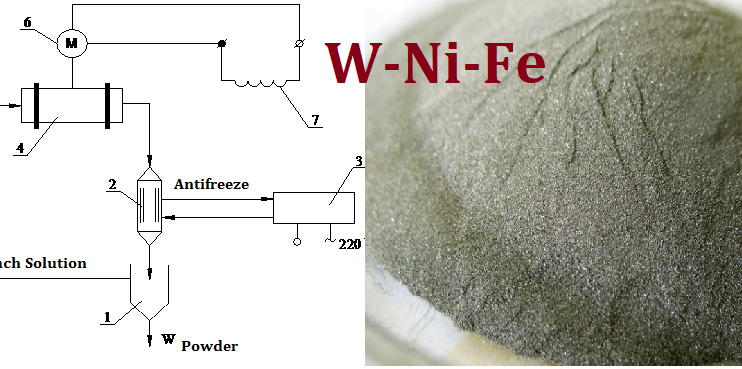
The work is devoted to the actual topic of processing scrap of the strategic alloy W-Ni-Fe, which is used in the production of armor-piercing projectiles. The recycling of tungsten and other alloy components solves the problem of scarcity and preciousness of these metals. In this work, the influence of the concentration of hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide, as components of the leaching solution, on the degree of leaching of the binding phase was investigated. It was established that an increase in the concentration of both components leads to an increase in the rate of both the leaching process and the course of side processes, which lead to an untargeted consumption of reagents. The results of the experimental studies show that the most effective is the use of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 2 mol/l and hydrogen peroxide with a concentration of 2 mol/l. The problem of catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is solved by carrying out the leaching process at a low temperature (about -5 °C). A new method of leaching W-Ni-Fe alloy to obtain high-quality tungsten powder is proposed. Intensification of the process is achieved by organizing leaching under self-grinding conditions with continuous mechanical renewal of the surface that is in contact with the acid-oxidizing leaching solution.
References
Shemi, A., Magumise, A., Ndlovu, S., Sacks, N. (2018). Recycling of tungsten carbide scrap metal: A review of recycling methods and future prospects. Minerals Engineering, 122, 195–205. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2018.03.036
Tang, L., Wang, P., Graedel, T. E., Pauliuk, S., Xiang, K., Ren, Y., & Chen, W.-Q. (2020). Refining the understanding of China’s tungsten dominance with dynamic material cycle analysis. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 158, 104829.
doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.1048
Liu, W., Li, Y., Zeng, D., Li, J., & Zhao, Z. (2018). Removal of Calcium from Scheelite Leaching Solution by Addition of CaSO4 Inoculating Crystals. J.O.M. 70, 2003–2007 doi:10.1007/s11837-018-2860-x
Tkaczyk, A. H., Bartl, A., Amato, A., Lapkovskis, V., Petranikova, M. (2018). Sustainability evaluation of essential critical raw materials: cobalt, niobium, tungsten and rare earth elements. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 51(20), 203001. doi:10.1088/1361-6463/aaba99
Shen, L., Li, X., Lindberg, D., Taskinen, P. (2019). Tungsten extractive metallurgy: A review of processes and their challenges for sustainability. Minerals Engineering, 142, 105934. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2019.105934
Polini, R., Marcucci, A., D’Ottavi, C., Nunziante, P., De Filippis, P., Marcheselli, G. (2021). Toward Greener Synthesis of WC Powders for Cemented Tungsten Carbides Manufacturing. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 9(25), 8458–8466. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c01286
Shen, L., Li, X., Lindberg, D., Taskinen, P. (2019). Tungsten extractive metallurgy: A review of processes and their challenges for sustainability. Minerals Engineering, 142, 105934. doi:10.1016/j.mineng.2019.105934
Liu, X., Deng, L., Chen, X., Li, J., He, L., Sun, F., Zhao, Z. (2021). Recovery of tungsten from acidic solutions rich in calcium and iron. Hydrometallurgy, 204, 105719. doi:10.1016/j.hydromet.2021.10571
Kumar, R.; Kariminejad, A.;Antonov, M.; Goljandin, D.; Klimczyk, P.; Hussainova, I. (2023). Progress in Sustainable Recycling and Circular Economy of Tungsten Carbide Hard Metal Scraps for Industry 5.0 and Onwards. Sustainability, 15, 12249. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612249
Masoudi, A., Abbaszadeh, H. (2013). Tungsten Direct Recovery from W-Cu Alloy Scrap by Selective Digestion via FeCl3 Aqueous Solution. American Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 1(1), 1–5.
Mulenshi, J., Chelgani, S. C., & Rosenkranz, J. (2021). Mechanochemical Treatment of Historical Tungsten Tailings: Leaching While Grinding for Tungsten Extraction Using NaOH. Sustainability, 13(6), 3258. doi:10.3390/su13063258
Leal-Ayala, D. R., Allwood, J. M., Petavratzi, E., Brown, T. J., Gunn, G. (2015). Mapping the global flow of tungsten to identify key material efficiency and supply security opportunities. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 103, 19–28. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.07.003
Ji, L., Yin, C., Chen, X., Liu, X., Zhao, Z. (2020). Hydrogen peroxide coordination-calcium salt precipitation for deep phosphorus removal from crude sodium tungstate solution. Hydrometallurgy, 191, 105189. doi:10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.105189
Luo, L., Miyazaki, T., Shibayama, A., Yen, W., Fujita, T. (2003). A novel process for recovery of tungsten and vanadium from a leach solution of tungsten alloy scrap. Minerals Engineering, 16(7), 665–670. doi:10.1016/s0892-6875(03)00103-1
Li, M., Liu, Q. Q., Xi, X. L., Nie, Z. R. (2017). A New Green Approach for Recovery of Metallic Tungsten through Electrolysis of Tungsten Carbide Scrap Anode in Molten Salts. Materials Science Forum, 898, 1871–1879. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.898.1871
Su, K., Ma, X., & Zhao, B. (2021). Harmless Treatment and Valuable Metals Recovery of Tungsten Leaching Residues: A Thermodynamic and Experimental Study. JOM, 73(6), 1937–1946. doi:10.1007/s11837-021-04682-2
Liao, C., Xie, S., Wang, X., Zhao, B., Cai, B., & Wang, L. (2021). Thermodynamic and Experimental Analyses of the Carbothermic Reduction of Tungsten Slag. JOM, 73(6), 1853–1860. doi:10.1007/s11837-021-04671-5
Katiyar, P. K., Randhawa, N. S. (2020). A comprehensive review on recycling methods for cemented tungsten carbide scraps highlighting the electrochemical techniques. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 90, 105251. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2020.105251
Liu, H., Liu, H., Nie, C., Zhang, J., Steenari, B.-M., Ekberg, C. (2020). Comprehensive treatments of tungsten slags in China: A critical review. Journal of Environmental Management, 270, 110927. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110927
Luo, L., Kejun, L., Shibayama, A., Yen, W., Fujita, T., Shindo, O., Katai, A. (2004). Recovery of tungsten and vanadium from tungsten alloy scrap. Hydrometallurgy, 72(1-2), 1–8. doi:10.1016/s0304-386x(03)00121-x
Jana, R. K., Kumar, V., Saha, A. K., Rao, K. V., Pandey, B. D., Premchand. (1996). Processing of Tungsten Alloy Scrap for the Recovery of Tungsten Metal. In: Proceedings of National Seminar on Environmental & Waste Management in Metallurgical Industries, Jamshedpur.
Srivastava, R. R., Lee, J., Bae, M., Kumar, V. (2018). Reclamation of tungsten from carbide scraps and spent materials. Journal of Materials Science, 2018, 1–25. doi:10.1007/s10853-018-2876-1
Sknar, Y.E., Amirulloeva, N.V., Sknar, I.V., Danylov, F.I. (2016). Electrodeposition of Ni–ZrO2 Nanocomposites from Methanesulfonate Electrolytes, Materials Science, 51(6), 877–884. doi:10.1007/s11003-016-9916-2
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Oles Honchar Dnipro National University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Authors reserve the right of attribution for the submitted manuscript, while transferring to the Journal the right to publish the article under the Creative Commons Attribution License. This license allows free distribution of the published work under the condition of proper attribution of the original authors and the initial publication source (i.e. the Journal)
- Authors have the right to enter into separate agreements for additional non-exclusive distribution of the work in the form it was published in the Journal (such as publishing the article on the institutional website or as a part of a monograph), provided the original publication in this Journal is properly referenced
- The Journal allows and encourages online publication of the manuscripts (such as on personal web pages), even when such a manuscript is still under editorial consideration, since it allows for a productive scientific discussion and better citation dynamics (see The Effect of Open Access).

